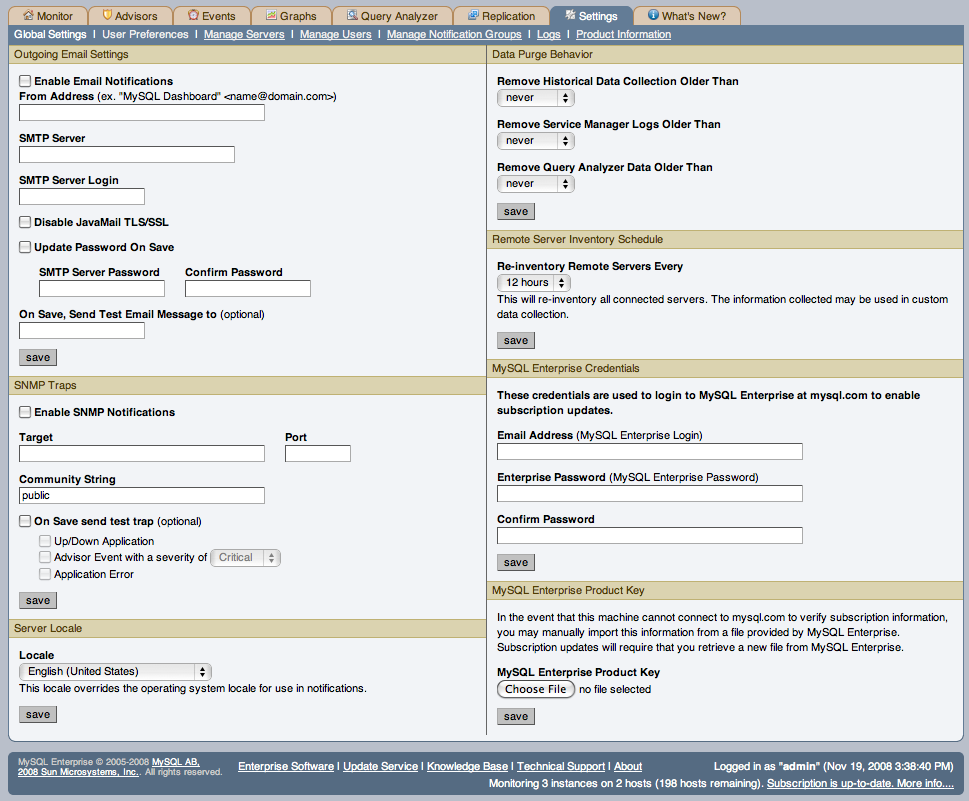
The Global Settings control the main confirguration parameters for the entire MySQL Enterprise Monitor system, including your email notifications, data purge, and Enterprise website credentials.
The Global Settings page is divided into a number of different sections:
-
Outgoing Email Settings
Configures the settings for email notifications by MySQL Enterprise Service Manager. You must configure the From Address SMTP Server settings. If your server requires authorization, complete the necessary server login details, and whether SSL is required.
You can test your configuration immediately by adding an email address to the On Save, Send Test Email Message to box.
For more information about
Outgoing Email Settingssee, Section 15.3.2.7.5, “Outgoing Email Settings”. -
The
SNMP Trapssection of theGlobal Preferencespage allows you to enable Simple Network Management Protocol so that your Network Management System (NMS) can handle events created by the MySQL Enterprise Monitor. Configure this section to route alerts and notifications to standard SNMP-enabled nodes on your network.In the target text box enter the IP address or the host name of your NMS listener. The port number defaults to the well-known SNMP port,
162. If you are not using this port, enter the port that your Network Management System is listening on.Enter the appropriate community string in the
Community Stringtext box. The default value for this string ispublic.To ensure that the target you have specified is valid, check the
On Save, Send Test Trapcheck box. The remaining check boxes help you to configure how your NMS responds to MySQL Enterprise Monitor. Check the Up/Down Application check box to configure NMS for starting up or shutting down the MySQL Enterprise Monitor. For configuration of advisor events choose a level of severity and check the Advisor event with the severity ofCriticalcheck box. Finally, choose the Application Error check box to configure NMS to support application error traps. Be sure to save your settings before exiting.If you wish to enable SNMP traps globally, check the
Enable SNMP Notificationscheckbox. To enable SNMP traps only for specific rules run against specific servers or server groups leave this checkbox unchecked — enabling specific SNMP traps is done as rules are scheduled. For instructions on doing this see Section 15.6.2, “Scheduling Rules”.The Management Information Base (MIB) file associated with SNMP trapping is called
MONITOR.MIB. For the location this file see The Management Information Base (MIB) File. -
The
Server Localesetting determines the language of notification for the following items:Email notifications
SNMP traps
The naming conventions for shared resources such as a replication group name prefix
The initial value in this drop down list box is the locale for the OS on which the Dashboard is running.
-
The
Data Purge Behaviorsection of theGlobal Preferencespage lets you remove old log files and also old data from the repository. The default purge interval isnever. If you wish to purge data, change this setting by choosing from the drop-down list. Choosing52 weeks, for example, will remove all data that is older than a year.Warning
Purging data will permanently remove information from the repository. Since events are derived from data contained in the repository, they will be purged along with the data.
Ensure that there is adequate disk space for the repository. If you are monitoring numerous servers and running many rules the size of the repository can increase rapidly. Choose purge behavior accordingly.
The default value for purging,
never, is the safest option. However, please choose a purge setting that makes sense for your environment.Note
The purge process is started approximately once every minute. If you change the purge duration from a larger timespan to a smaller one, the data may start to be purged immediately.
You can configure the data purge behavior for a number of different systems individually:
Remove Historical Data Collection Older Than configures the duration that the main data about your servers is retained. This includes all data collections, including CPU, memory and connections and activity statistics.
Remove Service Manager Logs Older Than configures the duration that the main MySQL Enterprise Service Manager logs are retained.
Remove Query Analyzer Data Older Than configures the duration that the query analyzer statistics and information about individual queries is retained.
Notes for setting purge behavior:
Purging can be carried out manually by enabling the
innodb_file_per_tablefor the repository database and then using anOPTIMIZE TABLEoperation to reclaim space from deleted rows in the table.
-
Remote Server Inventory Schedule
MySQL Enterprise Monitor keeps track of all the databases and tables in a server, as well as the amount of RAM, disk space, and other items. A re-inventory updates this information in case you have added or dropped databases and tables. Depending upon the configuration of your system, this operation can tax resources. If you are monitoring many remote servers this is an operation you may want to perform in off-peak hours only.
-
MySQL Enterprise Credentials
You can specify the credentials for logging into the MySQL Enterprise Website. These should match the user name and password that you have registered with MySQL for your enterprise subscription.
Note
Only administrators can change the
MySQL Enterprise Credentialssection or enter a product key; for other users, this section does not show up in the interface. For more information about different users and their rights see Section 15.5.4, “Managing Users”. Specifying incorrect credentials results in the error message, “Your credentials do not appear to be valid.” -
MySQL Enterprise Product Key
You may update your
MySQL Enterprise Product Key. If you do not have access to the Internet from the Dashboard, this provides an alternate way to update or activate the MySQL Enterprise Monitor.To enter your product key first download it from the MySQL Enterprise website. Copy the key to a location accessible from the Dashboard. Use the Browse button to locate the key and then press the save button.
If you wish to switch from using your MySQL Enterprise credentials to using a product key to update MySQL Enterprise Monitor, you must first clear your credentials. Do this by removing the email address from the MySQL Enterprise Credentials section and then clicking the save button. You may then enter and save your MySQL Enterprise product key.
Note
Only administrators can change the
MySQL Enterprise Credentialssection or enter a product key; for other users, this section does not show up in the interface. For more information about different users and their rights see Section 15.5.4, “Managing Users”. Specifying incorrect credentials results in the error message, “Your credentials do not appear to be valid.”

User Comments
Add your own comment.