Advanced MySQL Replication Techniques
Advanced MySQL Replication Techniques
by Giuseppe Maxia
04/20/2006
You may know about the MySQL Cluster, which is a complex architecture to achieve high availability and performance. One of the advantages of MySQL Cluster is that each node is a peer to the others, whereas in a normal replicating system you have a master and many slaves, and applications must be careful to write only to the master.
The main disadvantages of MySQL Cluster are (as of MySQL 5.0):
- The database is in memory only, thus requiring more resources than a normal MySQL database. (MySQL 5.1 introduces table spaces, with the capability of storing nonindexed data on disk.)
- Some normal features are not available, such as full-text searches, referential integrity, and transaction isolation levels higher than
READ COMMITTED.
There are some cases where the MySQL Cluster is the perfect solution, but for the vast majority, replication is still the best choice.
Replication, too, has its problems, though:
- There is a fastidious distinction between master and slaves. Your applications must be replication-aware, so that they will write on the master and read from the slaves. It would be so nice to have a replication array where you could use all the nodes in the same way, and every node could be at the same time master and slave.
- There is the fail-over problem. When the master fails, it's true that you have the slaves ready to replace it, but the process of detecting the failure and acting upon it requires the administrator's intervention.
Fixing these two misfeatures is exactly the purpose of this article. Using features introduced in MySQL 5.0 and 5.1, it is possible to build a replication system where all nodes act as master and slave at the same time, with a built-in fail-over mechanism.
Setting Up a Multimaster Replication System
For those of you not well acquainted with the replication basics, I can refer to an earlier article explaining MySQL replication, and the demanding reader can integrate with the dry but extensive official MySQL replication manual.
Back to business. Consider the situation where you set up a replication system with more than one master. This has been a common scenario over the past several years. Chapters 7 and 8 of Jeremy Zawodny's High Performance MySQL describe such a solution. At the time of the book's publication, though, the necessary technology was not yet available.
One hard-to-solve problem in a multimaster replication is the conflict that can happen with self-generated keys. The AUTO_INCREMENT feature is quite convenient, but in a replication environment it will be disruptive. If node A and node B both insert an auto-incrementing key on the same table, conflicts arise immediately.
Rescue comes with recent versions. MySQL 5 introduces a couple of server variables for replicated auto-increment that address this specific problem and allow for the creation of an array of peer-to-peer nodes with MySQL replication.
Quoting from the manual:
auto_increment_incrementcontrols the increment between successiveAUTO_INCREMENTvalues.auto_increment_offsetdetermines the starting point forAUTO_INCREMENTcolumn values.
By choosing non-conflicting values for these variables on different masters, servers in a multiple-master configuration will not use conflicting AUTO_INCREMENT values when inserting new rows into the same table. To set up N master servers, set the variables like this:
- Set
auto_increment_incrementto N on each master. - Set each of the N masters to have a different
auto_increment_offset, using the values 1, 2, ... , N.
Using those two variables as described in the manual, you can ensure that all nodes in your replication array will use different sequences of auto-incrementing numbers. For example, using auto_increment_increment = 10 and auto_increment_offset=3, the numbers generated when inserting three records will be 3, 13, 23. Using 10, 7, you'll get 7, 17, 27, and so on.
For my four-node array, I set auto_increment_increment to 10 for each node, and auto_increment_offset to 1 in the first node, 2 in the second, and so on.
This is theoretically clear, but it still isn't clear how I managed to transform these servers into peer-to-peer nodes.
The answer is a circular replication, where each node is master of the following node and slave of the preceding one.
Circular replication with two nodes
In its simplest form, circular replication has two nodes, where each one is at the same time master and slave of the other (Figure 1).
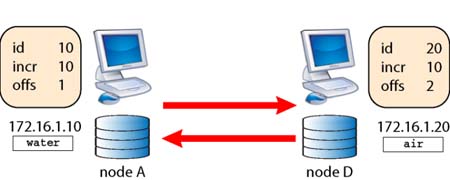
Figure 1. Circular replication between two nodes
For this test, I used two servers in my company (water and air; there will soon be two more, named fire and earth). Their basic configuration is:
# node A - (water) setup
[mysqld]
server-id = 10
# auto_increment_increment = 10
# auto_increment_offset = 1
master-host = air.stardata.it
master-user = nodeAuser
master-password = nodeApass
# node B - (air) setup
[mysqld]
server-id = 20
# auto_increment_increment = 10
# auto_increment_offset = 2
master-host = water.stardata.it
master-user = nodeBuser
master-password = nodeBpassNotice the two magic variables in the configuration files. If you omit such variables (or comment them, as in this example), then something nasty may happen, and the unfortunate circumstances are easy to demonstrate. Remember that MySQL replication is asynchronous. It means that the replication process in the slave can happen at a different time than the one taking place in the master. This feature makes replication more resilient and ensures that even if you suffer a connection breakdown between master and slave, replication will continue when the slave connection resumes. However, this feature has a nasty side effect when you deal with auto-incremented values. Assume that you have a table like this:
CREATE TABLE x (
id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
c char(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1Assume also that the connection between node A and node B breaks for a moment. Suppose you issue an INSERT statement in both servers, while the replication is not working and the auto_increment variables are not set:
[node A] insert into x values (null, 'aaa'), (null, 'bbb'), (null, 'ccc');
[node B] insert into x values (null, 'xxx'), (null, 'yyy'), (null, 'zzz');When replication resumes, you get a blocking error in both nodes:
Error 'Duplicate entry '1' for key 'PRIMARY'' on query. Default database:
'test'. Query: 'insert into x values (null, 'aaa')'The reason is easy to discover:
[node A] select * from x;
+----+------+
| id | c |
+----+------+
| 1 | aaa |
| 2 | bbb |
| 3 | ccc |
+----+------+
[node B] select * from x;
+----+------+
| id | c |
+----+------+
| 1 | xxx |
| 2 | yyy |
| 3 | zzz |
+----+------+Both nodes have produced the same primary keys. Thus, when replication resumed, the DBMS justly complained that there was a mistake. Now activate those two variables to see what happens.
[node A] set auto_increment_increment = 10;
[node A] set auto_increment_offset = 1;
[node B] set auto_increment_increment = 10;
[node B] set auto_increment_offset = 2;Clean the errors, delete all the records in the test table, and redo the insertion (after stopping the replication, to simulate a communication breakdown):
[node A] SET GLOBAL SQL_SLAVE_SKIP_COUNTER=1; start slave;
[node B] SET GLOBAL SQL_SLAVE_SKIP_COUNTER=1; start slave;
[node A] truncate x;
[node A] stop slave ;
[node B] stop slave ;
[node A] insert into x values (null, 'aaa'), (null, 'bbb'), (null, 'ccc');
[node B] insert into x values (null, 'xxx'), (null, 'yyy'), (null, 'zzz');Now the situation is different.
[node A] select * from x;
+-----+------+
| id | c |
+-----+------+
| 1 | aaa |
| 11 | bbb |
| 21 | ccc |
+-----+------+
[node B] select * from x;
+-----+------+
| id | c |
+-----+------+
| 2 | xxx |
| 12 | yyy |
| 22 | zzz |
+-----+------+Thus, when replication resumes, there is no conflicting error. This proves it. Choosing appropriate values for the auto_increment_increment and auto_increment_offset server variables prevents conflicts between auto-generated keys in this circular replication setup. QED.
To read the rest of this article, please visit ONLamp.com »

