- 2 Using MySQL with DRBD
- 2.1 Configuring the DRBD Environment
- 2.2 Configuring MySQL for DRBD
- 2.3 Optimizing Performance and Reliability
Because of the nature of the DRBD system, the critical requirements are for a very fast exchange of the information between the two hosts. To ensure that your DRBD setup is available to switch over in the event of a failure as quickly as possible, you must transfer the information between the two hosts using the fastest method available.
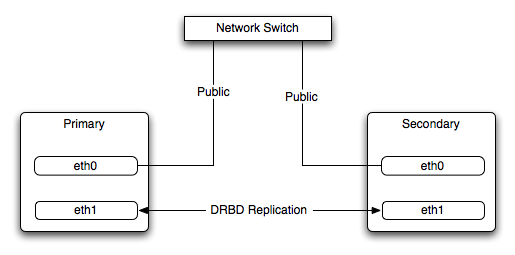
Typically, a dedicated network circuit should be used for exchanging DRBD data between the two hosts. You should then use a separate, additional, network interface for your standard network connection. For an example of this layout, see Figure 2.2, “DRBD Architecture Using Separate Network Interfaces”.
The dedicated DRBD network interfaces should be configured to use a nonrouted TCP/IP network configuration. For example, you might want to set the primary to use 192.168.0.1 and the secondary 192.168.0.2. These networks and IP addresses should not be part of normal network subnet.
Note
The preferred setup, whenever possible, is to use a direct cable connection (using a crossover cable with Ethernet, for example) between the two machines. This eliminates the risk of loss of connectivity due to switch failures.