- 4 MySQL Cluster Programs
- 4.1 MySQL Server Usage for MySQL Cluster
- 4.2 ndbd — The MySQL Cluster Data Node Daemon
- 4.3 ndbmtd — The MySQL Cluster Data Node Daemon (Multi-Threaded)
- 4.4 ndb_mgmd — The MySQL Cluster Management Server Daemon
- 4.5 ndb_mgm — The MySQL Cluster Management Client
- 4.6 ndb_config — Extract MySQL Cluster Configuration Information
- 4.7 ndb_cpcd — Automate Testing for NDB Development
- 4.8 ndb_delete_all — Delete All Rows from an NDB Table
- 4.9 ndb_desc — Describe NDB Tables
- 4.10 ndb_drop_index — Drop Index from an NDB Table
- 4.11 ndb_drop_table — Drop an NDB Table
- 4.12 ndb_error_reporter — NDB Error-Reporting Utility
- 4.13 ndb_print_backup_file — Print NDB Backup File Contents
- 4.14 ndb_print_schema_file — Print NDB Schema File Contents
- 4.15 ndb_print_sys_file — Print NDB System File Contents
- 4.16 ndbd_redo_log_reader — Check and Print Content of Cluster Redo Log
- 4.17 ndb_restore — Restore a MySQL Cluster Backup
- 4.18 ndb_select_all — Print Rows from an NDB Table
- 4.19 ndb_select_count — Print Row Counts for NDB Tables
- 4.20 ndb_show_tables — Display List of NDB Tables
- 4.21 ndb_size.pl — NDBCLUSTER Size Requirement Estimator
- 4.22 ndb_waiter — Wait for MySQL Cluster to Reach a Given Status
- 4.23 Options Common to MySQL Cluster Programs
This is a Perl script that can be used to estimate the amount
of space that would be required by a MySQL database if it were
converted to use the NDBCLUSTER
storage engine. Unlike the other utilities discussed in this
section, it does not require access to a MySQL Cluster (in
fact, there is no reason for it to do so). However, it does
need to access the MySQL server on which the database to be
tested resides.
Requirements:
A running MySQL server. The server instance does not have to provide support for MySQL Cluster.
A working installation of Perl.
The
DBImodule, which can be obtained from CPAN if it is not already part of your Perl installation. (Many Linux and other operating system distributions provide their own packages for this library.)Previous to MySQL 5.1.18, ndb_size.pl also required the
HTML::Templatemodule and an associated template fileshare/mysql/ndb_size.tmpl. Beginning with MySQL 5.1.18,ndb_size.tmplis no longer needed (or included).A MySQL user account having the necessary privileges. If you do not wish to use an existing account, then creating one using
GRANT USAGE ON— wheredb_name.*db_nameis the name of the database to be examined — is sufficient for this purpose.
ndb_size.pl can also be found in the
MySQL sources in storage/ndb/tools. If
this file is not present in your MySQL installation, you can
obtain it from the
MySQL
Forge project page.
The following table includes options that are specific to the MySQL Cluster program ndb_size.pl. Additional descriptions follow the table. For options common to all MySQL Cluster programs, see Section 4.23, “Options Common to MySQL Cluster Programs”.
Table 4.8. ndb_size.pl Command Line Options
| Format | Description | Introduction | Deprecated | Removed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| --database=dbname | The databae or databases to examine; accepts a comma-delimited list; the default is ALL (use all databases found on the server) | |||
| --excludedbs=db-list | Skip any databases in a comma-separated list of databases | |||
| --excludetables=tbl-list | Skip any tables in a comma-separated list of tables | |||
| --format=string | Set output format (text or HTML) | |||
| --hostname[:port] | Specify host and optional port as host[:port] | |||
| --loadqueries=file | Loads all queries from the file specified; does not connect to a database | |||
| --password=string | Specify a MySQL user password | |||
| --real_table_name=table | Designates a table to handle unique index size calculations | 5.1.22-ndb-6.2.5 | ||
| --savequeries=file | Saves all queries to the database into the file specified | |||
| --socket=file | Specify a socket to connect to | 5.1.22-ndb-6.2.5 | ||
| --user=string | Specify a MySQL user name |
Usage:
perl ndb_size.pldb_name|ALL] [--hostname=host[:port]] [--socket=socket] [--user=user] \ [--password=password] [--help|-h] [--format=(html|text)] [--loadqueries=file_name] [--savequeries=file_name]
By default, this utility attempts to analyze all databases on
the server. You can specify a single database using the
--database option; the default behavior can
be made explicit by using ALL for the name
of the database. You can also exclude one or more databases by
using the --excludedbs with a comma-separated
list of the names of the databases to be skipped. Similarly,
you can cause specific tables to be skipped by listing their
names, separated by commas, following the optional
--excludetables option. A host name (and
possibly a port as well) can be specified using
--hostname; the default is
localhost:3306. If necessary, you can
specify a socket; the default is
/var/lib/mysql.sock. A MySQL user name
and password can be specified the corresponding options shown.
It also possible to control the format of the output using the
--format option; this can take either of the
values html or text,
with text being the default. An example of
the text output is shown here:
shell> ndb_size.pl --database=test --socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
ndb_size.pl report for database: 'test' (1 tables)
--------------------------------------------------
Connected to: DBI:mysql:host=localhost;mysql_socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
Including information for versions: 4.1, 5.0, 5.1
test.t1
-------
DataMemory for Columns (* means varsized DataMemory):
Column Name Type Varsized Key 4.1 5.0 5.1
HIDDEN_NDB_PKEY bigint PRI 8 8 8
c2 varchar(50) Y 52 52 4*
c1 int(11) 4 4 4
-- -- --
Fixed Size Columns DM/Row 64 64 12
Varsize Columns DM/Row 0 0 4
DataMemory for Indexes:
Index Name Type 4.1 5.0 5.1
PRIMARY BTREE 16 16 16
-- -- --
Total Index DM/Row 16 16 16
IndexMemory for Indexes:
Index Name 4.1 5.0 5.1
PRIMARY 33 16 16
-- -- --
Indexes IM/Row 33 16 16
Summary (for THIS table):
4.1 5.0 5.1
Fixed Overhead DM/Row 12 12 16
NULL Bytes/Row 4 4 4
DataMemory/Row 96 96 48 (Includes overhead, bitmap and indexes)
Varsize Overhead DM/Row 0 0 8
Varsize NULL Bytes/Row 0 0 4
Avg Varside DM/Row 0 0 16
No. Rows 0 0 0
Rows/32kb DM Page 340 340 680
Fixedsize DataMemory (KB) 0 0 0
Rows/32kb Varsize DM Page 0 0 2040
Varsize DataMemory (KB) 0 0 0
Rows/8kb IM Page 248 512 512
IndexMemory (KB) 0 0 0
Parameter Minimum Requirements
------------------------------
* indicates greater than default
Parameter Default 4.1 5.0 5.1
DataMemory (KB) 81920 0 0 0
NoOfOrderedIndexes 128 1 1 1
NoOfTables 128 1 1 1
IndexMemory (KB) 18432 0 0 0
NoOfUniqueHashIndexes 64 0 0 0
NoOfAttributes 1000 3 3 3
NoOfTriggers 768 5 5 5
For debugging purposes, the Perl arrays containing the queries
run by this script can be read from the file specified using
can be saved to a file using --savequeries; a
file containing such arrays to be read in during script
execution can be specified using
--loadqueries. Neither of these options has a
default value.
To produce output in HTML format, use the
--format option and redirect the output to a
file, as shown in this example:
shell> ndb_size.pl --database=test --socket=/tmp/mysql.sock --format=html > ndb_size.html
(Without the redirection, the output is sent to
stdout.) This figure shows a portion of the
generated ndb_size.html output file, as
viewed in a Web browser:
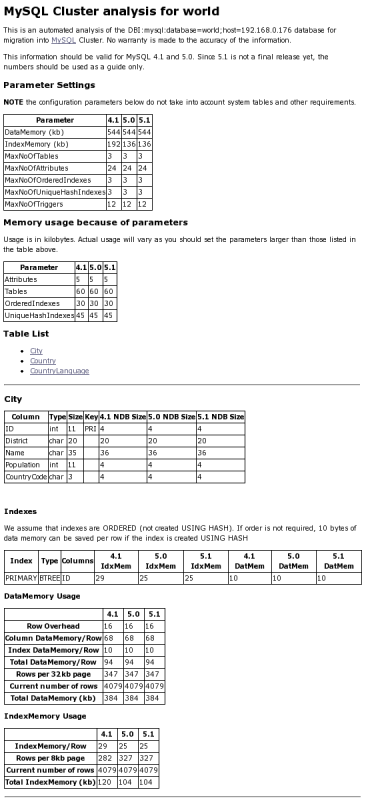
The output from this script includes:
Minimum values for the
DataMemory,IndexMemory,MaxNoOfTables,MaxNoOfAttributes,MaxNoOfOrderedIndexes,MaxNoOfUniqueHashIndexes, andMaxNoOfTriggersconfiguration parameters required to accommodate the tables analyzed.Memory requirements for all of the tables, attributes, ordered indexes, and unique hash indexes defined in the database.
The
IndexMemoryandDataMemoryrequired per table and table row.
