themis contain extra steps for the recipes package for dealingwith unbalanced data. The name themis is that of the ancient Greek god who is typically depicted with a balance.

You can install the released version of themis from CRAN with:
Install the development version from GitHub with:
Following is a example of using the SMOTE algorithm to deal with unbalanced data
library(recipes)
library(modeldata)
library(themis)
data(okc)
sort(table(okc$Class, useNA = "always"))
#>
#> <NA> stem other
#> 0 9539 50316
ds_rec <- recipe(Class ~ age + height, data = okc) %>%
step_meanimpute(all_predictors()) %>%
step_smote(Class) %>%
prep()
sort(table(juice(ds_rec)$Class, useNA = "always"))
#>
#> <NA> stem other
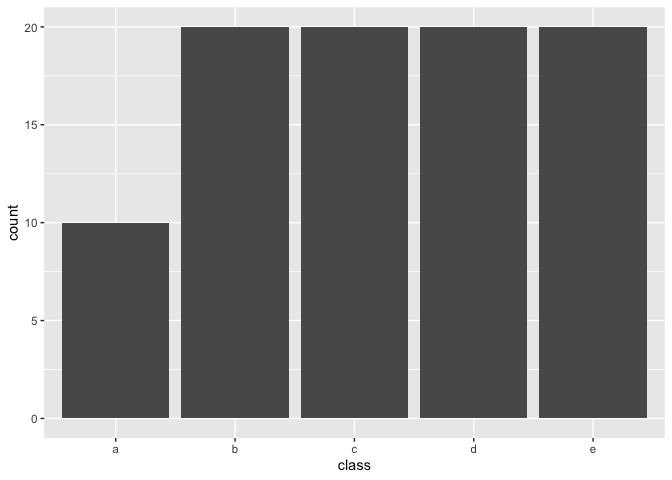
#> 0 50316 50316Below is some unbalanced data. Used for examples latter.
example_data <- data.frame(class = letters[rep(1:5, 1:5 * 10)],
x = rnorm(150))
library(ggplot2)
example_data %>%
ggplot(aes(class)) +
geom_bar()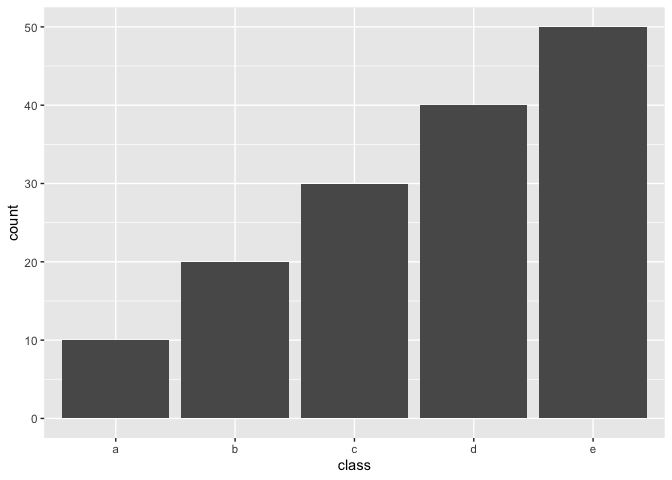
The following methods all share the tuning parameter over_ratio, which is the ratio of the majority-to-minority frequencies.
| name | function | Multi-class |
|---|---|---|
| Random minority over-sampling with replacement | step_upsample() |
:heavy_check_mark: |
| Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique | step_smote() |
:heavy_check_mark: |
| Borderline SMOTE-1 | step_bsmote(method = 1) |
:heavy_check_mark: |
| Borderline SMOTE-2 | step_bsmote(method = 2) |
:heavy_check_mark: |
| Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning | step_adasyn() |
:heavy_check_mark: |
| Generation of synthetic data by Randomly Over Sampling Examples | step_rose() |
By setting over_ratio = 1 you bring the number of samples of all minority classes equal to 100% of the majority class.
recipe(~., example_data) %>%
step_upsample(class, over_ratio = 1) %>%
prep() %>%
juice() %>%
ggplot(aes(class)) +
geom_bar()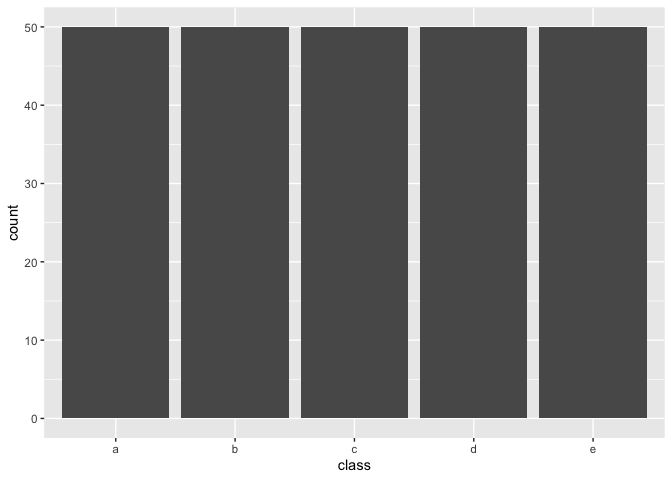
and by setting over_ratio = 0.5 we upsample any minority class with less samples then 50% of the majority up to have 50% of the majority.
recipe(~., example_data) %>%
step_upsample(class, over_ratio = 0.5) %>%
prep() %>%
juice() %>%
ggplot(aes(class)) +
geom_bar()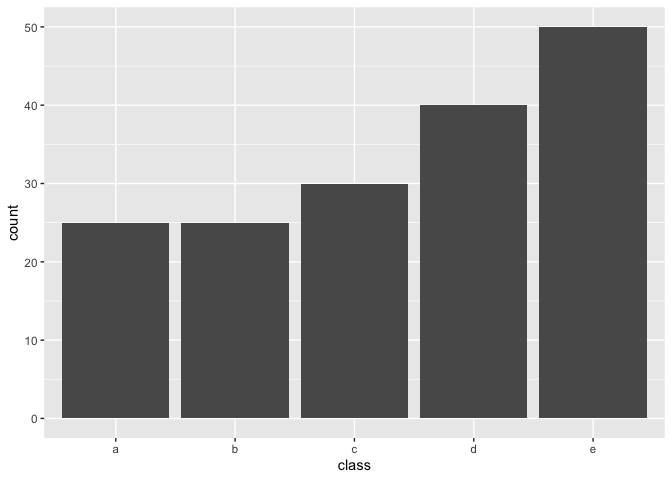
Most of the the following methods all share the tuning parameter under_ratio, which is the ratio of the minority-to-majority frequencies.
| name | function | Multi-class | under_ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random majority under-sampling with replacement | step_downsample() |
:heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| NearMiss-1 | step_nearmiss() |
:heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| Extraction of majority-minority Tomek links | step_tomek() |
By setting under_ratio = 1 you bring the number of samples of all majority classes equal to 100% of the minority class.
recipe(~., example_data) %>%
step_downsample(class, under_ratio = 1) %>%
prep() %>%
juice() %>%
ggplot(aes(class)) +
geom_bar()
and by setting under_ratio = 2 we downsample any majority class with more then 200% samples of the minority class down to have to 200% samples of the minority.
recipe(~., example_data) %>%
step_downsample(class, under_ratio = 2) %>%
prep() %>%
juice() %>%
ggplot(aes(class)) +
geom_bar()