

R client for accessing Twitter’s REST and stream APIs. Check out the rtweet package documentation website.
There are several R packages for interacting with Twitter’s APIs. See how {rtweet} compares to these others in the chart below.
| Task | rtweet | streamR | RTwitterAPI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Available on CRAN | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Updated since 2016 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Non-‘developer’ access | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Extended tweets (280 chars) | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Parses JSON data | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Converts to data frames | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Automated pagination | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Search tweets | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Search users | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Stream sample | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Stream keywords | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Stream users | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Get friends | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Get timelines | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get mentions | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get favorites | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get trends | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get list members | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get list memberships | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get list statuses | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get list subscribers | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get list subscriptions | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get list users | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Lookup collections | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Lookup friendships | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Lookup statuses | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Lookup users | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get retweeters | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Get retweets | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❓ |
| Post tweets | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Post favorite | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Post follow | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Post messsage | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Post mute | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Premium 30 day | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Premium full archive | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Run package tests | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
{{rtweet}} should be used in strict accordance with Twitter’s developer terms.
To get the current released version from CRAN:
To get the current development version from Github:
## install remotes package if it's not already
if (!requireNamespace("remotes", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("remotes")
}
## install dev version of rtweet from github
remotes::install_github("ropensci/rtweet")
## load rtweet package
library(rtweet)All you need is a Twitter account (user name and password) and you can be up in running in minutes!
Simply send a request to Twitter’s API (with a function like search_tweets(), get_timeline(), get_followers(), get_favorites(), etc.) during an interactive session of R, authorize the embedded rstats2twitter app (approve the browser popup), and your token will be created and saved/stored (for future sessions) for you!
All users must be authorized to interact with Twitter’s APIs. To become authorized, simply use a function like search_tweets(), get_timeline(), get_followers(), or get_favorites() in an interactive session an authorize via web browser popup on behalf of your Twitter account!
It is no longer necessary to obtain a developer account and create your own Twitter application to use Twitter’s API. You may still choose to do this (gives you more stability and permissions; see the table at the bottom of this section), but {rtweet} should work out of the box assuming (a) you are working in an interactive/live session of R and (b) you have installed the {httpuv} package.
auth vignette (or the API authorization section below) for additional instructions: https://rtweet.info/articles/auth.html.| Task | rstats2twitter | user-app |
|---|---|---|
| Work interactively | ✅ | ✅ |
| Search/lookup tweets/users | ✅ | ✅ |
| Get friends/followers | ✅ | ✅ |
| Get timelines/favorites | ✅ | ✅ |
| Get lists/collections | ✅ | ✅ |
| Post tweets | ❌ | ✅ |
| Run package tests | ❌ | ✅ |
| Use Bearer token | ❌ | ✅ |
| Read/Write Direct Messages | ❌ | ✅ |
Obtaining and using Twitter API tokens
Quick overview of rtweet package
Troubleshooting common rtweet problems
Search for up to 18,000 (non-retweeted) tweets containing the rstats hashtag.
## search for 18000 tweets using the rstats hashtag
rt <- search_tweets(
"#rstats", n = 18000, include_rts = FALSE
)Quickly visualize frequency of tweets over time using ts_plot().
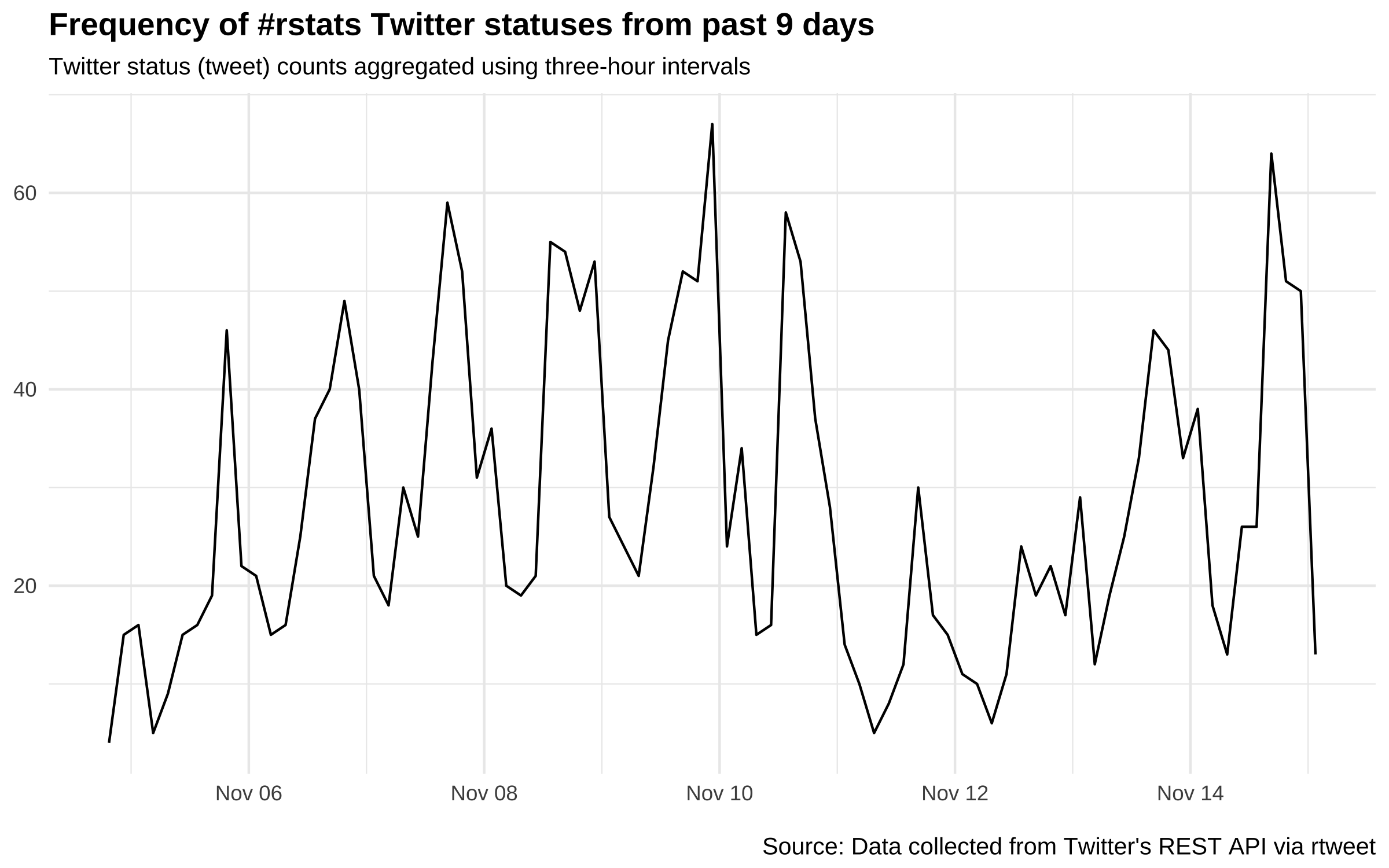
## plot time series of tweets
rt %>%
ts_plot("3 hours") +
ggplot2::theme_minimal() +
ggplot2::theme(plot.title = ggplot2::element_text(face = "bold")) +
ggplot2::labs(
x = NULL, y = NULL,
title = "Frequency of #rstats Twitter statuses from past 9 days",
subtitle = "Twitter status (tweet) counts aggregated using three-hour intervals",
caption = "\nSource: Data collected from Twitter's REST API via rtweet"
)
Twitter rate limits cap the number of search results returned to 18,000 every 15 minutes. To request more than that, simply set retryonratelimit = TRUE and rtweet will wait for rate limit resets for you.
## search for 250,000 tweets containing the word data
rt <- search_tweets(
"data", n = 250000, retryonratelimit = TRUE
)Search by geo-location—for example, find 10,000 tweets in the English language sent from the United States. Note: lookup_coords() requires users have a Google API key
## search for 10,000 tweets sent from the US
rt <- search_tweets(
"lang:en", geocode = lookup_coords("usa"), n = 10000
)
## create lat/lng variables using all available tweet and profile geo-location data
rt <- lat_lng(rt)
## plot state boundaries
par(mar = c(0, 0, 0, 0))
maps::map("state", lwd = .25)
## plot lat and lng points onto state map
with(rt, points(lng, lat, pch = 20, cex = .75, col = rgb(0, .3, .7, .75)))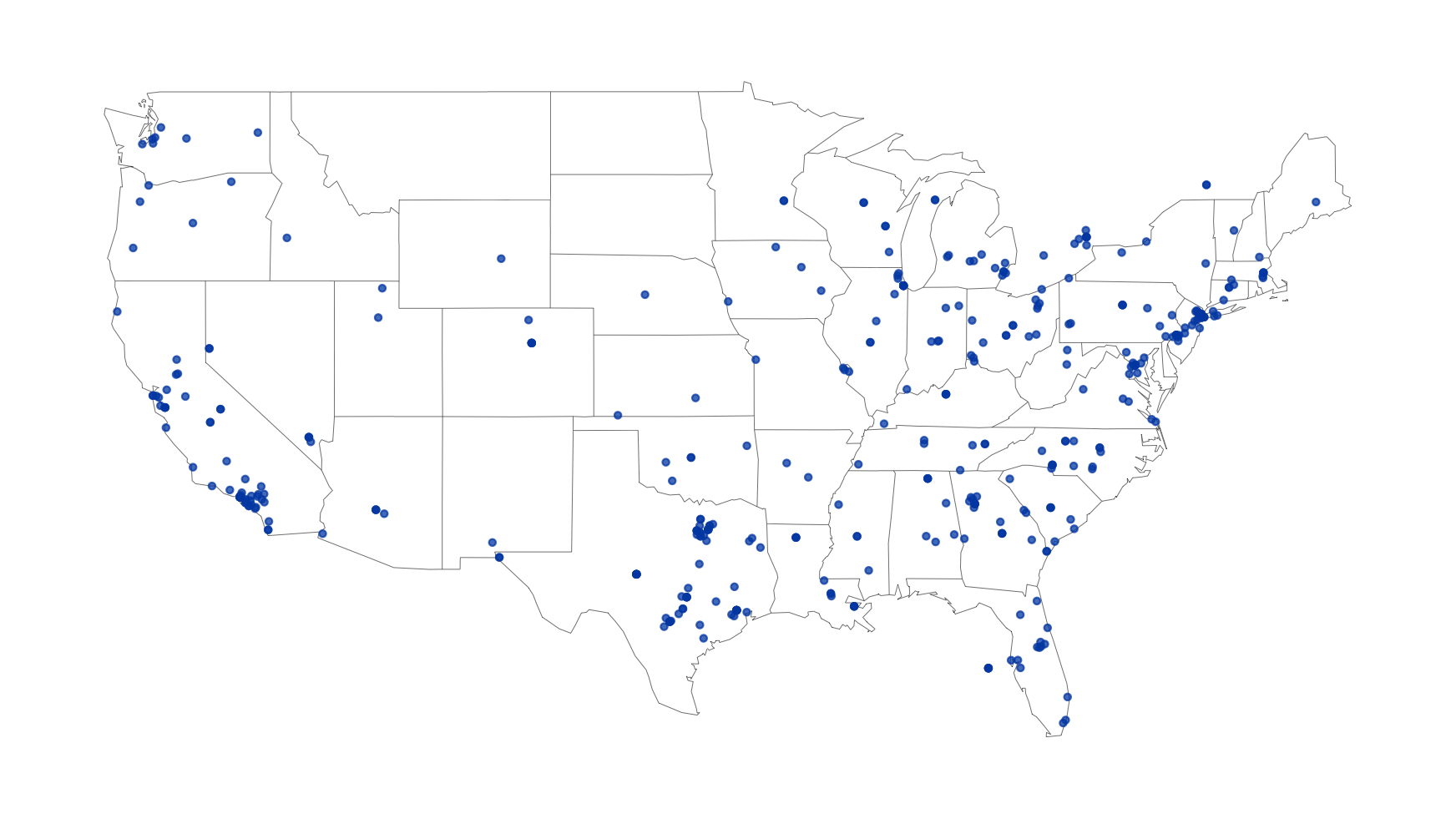
Randomly sample (approximately 1%) from the live stream of all tweets.
Stream all geo enabled tweets from London for 60 seconds.
## stream tweets from london for 60 seconds
rt <- stream_tweets(lookup_coords("london, uk"), timeout = 60)Stream all tweets mentioning realDonaldTrump or Trump for a week.
## stream london tweets for a week (60 secs x 60 mins * 24 hours * 7 days)
stream_tweets(
"realdonaldtrump,trump",
timeout = 60 * 60 * 24 * 7,
file_name = "tweetsabouttrump.json",
parse = FALSE
)
## read in the data as a tidy tbl data frame
djt <- parse_stream("tweetsabouttrump.json")Retrieve a list of all the accounts a user follows.
## get user IDs of accounts followed by CNN
cnn_fds <- get_friends("cnn")
## lookup data on those accounts
cnn_fds_data <- lookup_users(cnn_fds$user_id)Retrieve a list of the accounts following a user.
## get user IDs of accounts following CNN
cnn_flw <- get_followers("cnn", n = 75000)
## lookup data on those accounts
cnn_flw_data <- lookup_users(cnn_flw$user_id)Or if you really want ALL of their followers:
## how many total follows does cnn have?
cnn <- lookup_users("cnn")
## get them all (this would take a little over 5 days)
cnn_flw <- get_followers(
"cnn", n = cnn$followers_count, retryonratelimit = TRUE
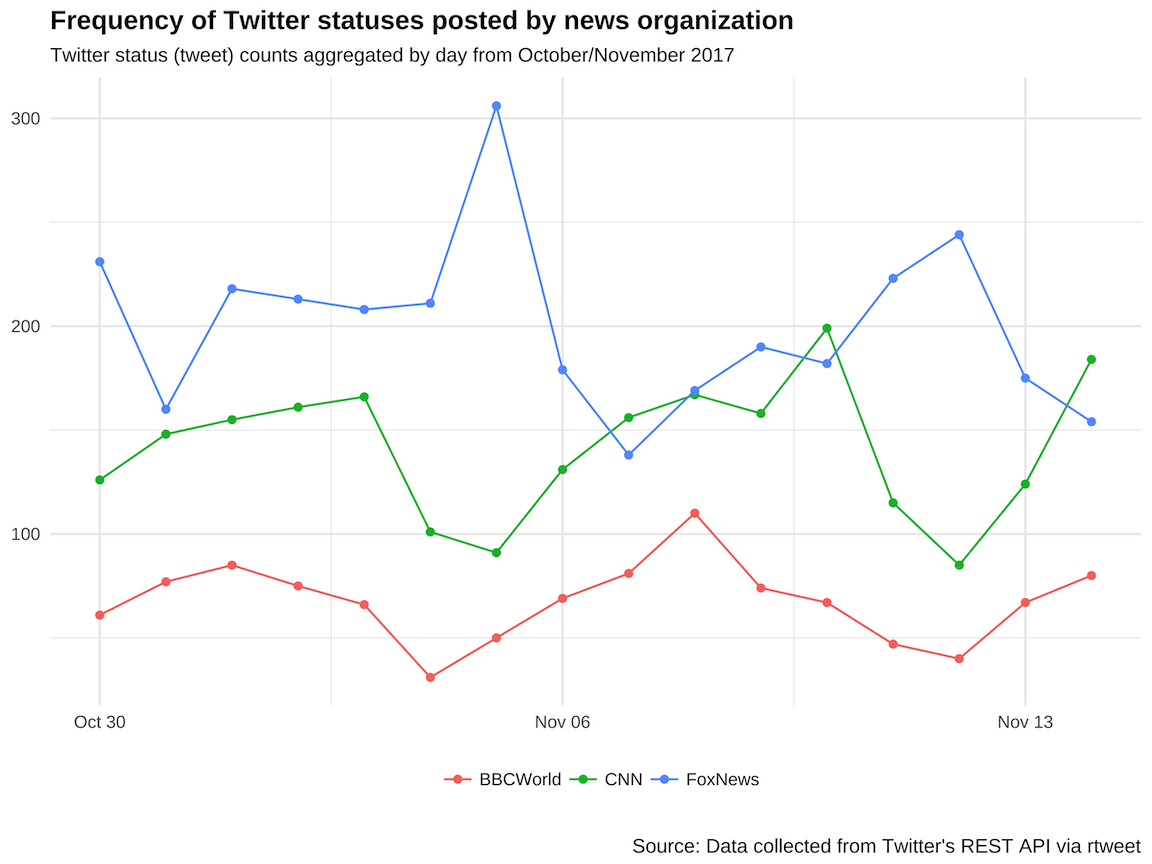
)Get the most recent 3,200 tweets from cnn, BBCWorld, and foxnews.
## get user IDs of accounts followed by CNN
tmls <- get_timelines(c("cnn", "BBCWorld", "foxnews"), n = 3200)
## plot the frequency of tweets for each user over time
tmls %>%
dplyr::filter(created_at > "2017-10-29") %>%
dplyr::group_by(screen_name) %>%
ts_plot("days", trim = 1L) +
ggplot2::geom_point() +
ggplot2::theme_minimal() +
ggplot2::theme(
legend.title = ggplot2::element_blank(),
legend.position = "bottom",
plot.title = ggplot2::element_text(face = "bold")) +
ggplot2::labs(
x = NULL, y = NULL,
title = "Frequency of Twitter statuses posted by news organization",
subtitle = "Twitter status (tweet) counts aggregated by day from October/November 2017",
caption = "\nSource: Data collected from Twitter's REST API via rtweet"
)
Get the 3,000 most recently favorited statuses by JK Rowling.
Search for 1,000 users with the rstats hashtag in their profile bios.
Discover what’s currently trending in San Francisco.
Communicating with Twitter’s APIs relies on an internet connection, which can sometimes be inconsistent. With that said, if you encounter an obvious bug for which there is not already an active issue, please create a new issue with all code used (preferably a reproducible example) on Github.