The rmdcev R package estimates and simulates multiple discrete-continuous extreme value (MDCEV) demand models with observed and unobserved individual heterogneity. Fixed parameter, latent class, and random parameter models can be estimated. These models are estimated using maximum likelihood or Bayesian estimation techniques and are implemented in Stan, which is a C++ package for performing full Bayesian inference (see http://mc-stan.org/). The package also includes functions for simulating demand and welfare outcomes from policy scenarios.
Development is in progress. Currently users can estimate the following models:
Under development
I recommend you first install rstan and C++ toolchain by following these steps:
https://github.com/stan-dev/rstan/wiki/RStan-Getting-Started
Once rstan is installed, you can install the released version of rmdcev from GitHub using devtools
if (!require(devtools)) {
install.packages("devtools")
library(devtools)
}
install_github("plloydsmith/rmdcev", build_vignettes = FALSE)Depending on your computer set-up, you may need to adjust your Makevars file of the .R folder (usually in your computer user folder) to ensure the first two lines are
You can switch build_vignettes to TRUE but it will take a lot longer to install. If installation fails, please let me know by filing an issue.
For more details on the model specification and estimation:
Bhat, C.R. (2008) “The Multiple Discrete-Continuous Extreme Value (MDCEV) Model: Role of Utility Function Parameters, Identification Considerations, and Model Extensions.” Transportation Research Part B, 42(3): 274-303.
For more details on the welfare simulation:
Lloyd-Smith, P (2018). “A New Approach to Calculating Welfare Measures in Kuhn-Tucker Demand Models.” Journal of Choice Modeling, 26: 19-27
As an example, we can simulate some data using the Hybrid specification. In this example, we are simulating data for 1000 invdividuals and 10 non-numeraire alternatives.
library(pacman)
p_load(tidyverse, rmdcev)
model <- "hybrid"
nobs <- 1000
nalts <- 10
sim.data <- GenerateMDCEVData(model = model, nobs = nobs, nalts = nalts)
#> Checking data...
#> Data is goodEstimate model using MLE
mdcev_est <- mdcev(~ b1 + b2 + b3 + b4 + b5 + b6 + b7 + b8-1,
data = sim.data$data,
model = model,
algorithm = "MLE")
#> Using MLE to estimate MDCEV
#> Chain 1: Initial log joint probability = -9033.01
#> Chain 1: Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
#> Chain 1: 19 -7445.3 0.511435 61.5753 1 1 26
#> Chain 1: Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
#> Chain 1: 39 -7401.21 0.136793 26.4292 1 1 47
#> Chain 1: Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
#> Chain 1: 59 -7395.55 0.00714899 6.06841 0.377 0.377 73
#> Chain 1: Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
#> Chain 1: 79 -7395.22 0.0361296 3.24521 1 1 97
#> Chain 1: Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
#> Chain 1: 99 -7395.13 0.00810581 2.07142 0.2972 1 118
#> Chain 1: Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
#> Chain 1: 119 -7395.12 0.00245304 0.176321 1 1 141
#> Chain 1: Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
#> Chain 1: 123 -7395.12 0.000199104 0.14664 0.3024 1 147
#> Chain 1: Optimization terminated normally:
#> Chain 1: Convergence detected: relative gradient magnitude is below toleranceSummarize results
summary(mdcev_est)
#> Model run using rmdcev for R, version 1.1.0
#> Estimation method : MLE
#> Model type : hybrid specification
#> Number of classes : 1
#> Number of individuals : 499
#> Number of non-numeraire alts : 10
#> Estimated parameters : 20
#> LL : -7395.12
#> AIC : 14830.24
#> BIC : 14914.49
#> Standard errors calculated using : 50 MVN draws
#> Exit of MLE : successful convergence
#> Time taken (hh:mm:ss) : 00:00:0.7
#>
#> Average consumption of non-numeraire alternatives:
#> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
#> 15.43 19.36 8.32 6.25 20.97 31.69 34.04 35.23 14.96 10.91
#>
#> Parameter estimates --------------------------------
#> Estimate Std.err z.stat
#> psi_b1 -4.512 0.738 -6.11
#> psi_b2 0.500 0.108 4.62
#> psi_b3 1.926 0.157 12.25
#> psi_b4 -1.579 0.172 -9.16
#> psi_b5 2.839 0.219 12.96
#> psi_b6 -1.787 0.173 -10.31
#> psi_b7 0.902 0.120 7.50
#> psi_b8 1.911 0.174 11.01
#> gamma1 1.925 0.557 3.46
#> gamma2 1.366 0.266 5.15
#> gamma3 1.548 0.383 4.05
#> gamma4 3.178 1.021 3.11
#> gamma5 1.661 0.318 5.22
#> gamma6 1.185 0.261 4.53
#> gamma7 1.672 0.311 5.37
#> gamma8 1.446 0.245 5.90
#> gamma9 1.388 0.252 5.50
#> gamma10 1.897 0.446 4.25
#> alpha1 0.514 0.037 13.72
#> scale 0.944 0.071 13.28
#> Note: Alpha parameter is equal for all alternatives.Compare estimates to true values
parms_true <- tbl_df(sim.data$parms_true) %>%
mutate(true = as.numeric(true))
output <- tbl_df(mdcev_est[["stan_fit"]][["theta_tilde"]]) %>%
dplyr::select(-tidyselect::starts_with("log_like"),
-tidyselect::starts_with("sum_log_lik"))
names(output)[1:mdcev_est$parms_info$n_vars$n_parms_total] <- mdcev_est$parms_info$parm_names$all_names
output<- output %>%
tibble::rowid_to_column("sim_id") %>%
tidyr::gather(parms, value, -sim_id)
coefs <- output %>%
mutate(parms = gsub("\\[|\\]", "", parms)) %>%
group_by(parms) %>%
summarise(mean = mean(value),
sd = sd(value),
zstat = mean / sd,
cl_lo = quantile(value, 0.025),
cl_hi = quantile(value, 0.975)) %>%
left_join(parms_true, by = "parms") %>%
print(n=200)
#> # A tibble: 20 x 7
#> parms mean sd zstat cl_lo cl_hi true
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 alpha1 0.514 0.0375 13.7 0.427 0.575 0.5
#> 2 gamma1 1.93 0.557 3.46 1.22 3.26 1.96
#> 3 gamma10 1.90 0.446 4.25 1.19 2.86 1.84
#> 4 gamma2 1.37 0.266 5.15 0.971 1.88 1.03
#> 5 gamma3 1.55 0.383 4.05 0.926 2.49 1.75
#> 6 gamma4 3.18 1.02 3.11 1.75 5.05 1.99
#> 7 gamma5 1.66 0.318 5.22 1.17 2.31 1.54
#> 8 gamma6 1.18 0.261 4.53 0.831 1.77 1.26
#> 9 gamma7 1.67 0.311 5.37 1.24 2.31 1.51
#> 10 gamma8 1.45 0.245 5.90 1.01 1.92 1.42
#> 11 gamma9 1.39 0.252 5.50 0.923 1.88 1.54
#> 12 psi_b1 -4.51 0.738 -6.11 -6.19 -3.45 -5
#> 13 psi_b2 0.500 0.108 4.62 0.304 0.707 0.5
#> 14 psi_b3 1.93 0.157 12.2 1.68 2.24 2
#> 15 psi_b4 -1.58 0.172 -9.16 -1.92 -1.28 -1.5
#> 16 psi_b5 2.84 0.219 13.0 2.50 3.32 3
#> 17 psi_b6 -1.79 0.173 -10.3 -2.10 -1.46 -2
#> 18 psi_b7 0.902 0.120 7.50 0.679 1.12 1
#> 19 psi_b8 1.91 0.174 11.0 1.59 2.26 2
#> 20 scale 0.944 0.0711 13.3 0.833 1.11 1Compare outputs using a figure
coefs %>%
ggplot(aes(y = mean, x = true)) +
geom_point(size=2) +
geom_text(label=coefs$parms) +
geom_abline(slope = 1) +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin=cl_lo,ymax=cl_hi,width=0.2))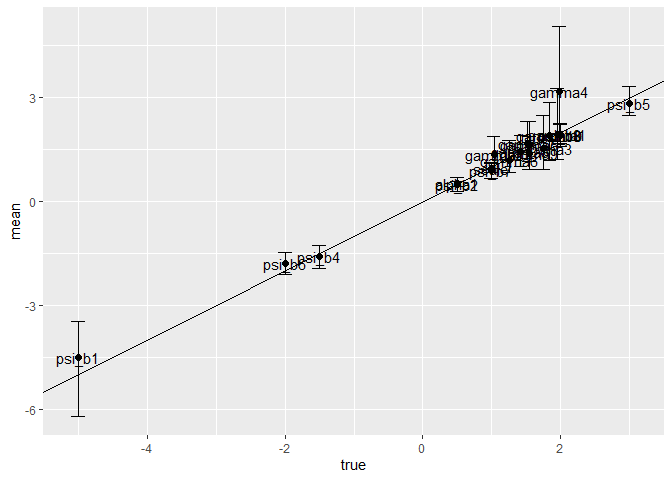
Create policy simulations (these are ‘no change’ policies with no effects)
npols <- 2 # Choose number of policies
policies<- CreateBlankPolicies(npols, nalts, mdcev_est$stan_data[["dat_psi"]], price_change_only = TRUE)
df_sim <- PrepareSimulationData(mdcev_est, policies)Simulate welfare changes
wtp <- mdcev.sim(df_sim$df_indiv,
df_common = df_sim$df_common,
sim_options = df_sim$sim_options,
cond_err = 1,
nerrs = 5,
sim_type = "welfare")
#> Using hybrid approach to simulation
#> Compiling simulation code
#> Simulating welfare...
#>
#> 1.50e+05simulations finished in0.03minutes.(71971per second)
summary(wtp)
#> # A tibble: 2 x 5
#> policy mean std.dev `ci_lo2.5%` `ci_hi97.5%`
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 policy1 1.09e-11 8.26e-11 -1.10e-10 1.47e-10
#> 2 policy2 1.09e-11 8.26e-11 -1.10e-10 1.47e-10