The goal of bench is to benchmark code, tracking execution time, memory allocations and garbage collections.
You can install the release version from CRAN with:
Or you can install the development version from GitHub with:
bench::mark() is used to benchmark one or a series of expressions, we feel it has a number of advantages over alternatives.
bench::press(), which allows you to easily perform and combine benchmarks across a large grid of values.The times and memory usage are returned as custom objects which have human readable formatting for display (e.g. 104ns) and comparisons (e.g. x$mem_alloc > "10MB").
There is also full support for plotting with ggplot2 including custom scales and formatting.
bench::mark()Benchmarks can be run with bench::mark(), which takes one or more expressions to benchmark against each other.
bench::mark() will throw an error if the results are not equivalent, so you don’t accidentally benchmark inequivalent code.
bench::mark(
dat[dat$x > 500, ],
dat[which(dat$x > 499), ],
subset(dat, x > 500))
#> Error: Each result must equal the first result:
#> `dat[dat$x > 500, ]` does not equal `dat[which(dat$x > 499), ]`Results are easy to interpret, with human readable units.
bnch <- bench::mark(
dat[dat$x > 500, ],
dat[which(dat$x > 500), ],
subset(dat, x > 500))
bnch
#> # A tibble: 3 x 6
#> expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
#> <bch:expr> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
#> 1 dat[dat$x > 500, ] 408µs 467µs 2079. 377KB 6.64
#> 2 dat[which(dat$x > 500), ] 284µs 354µs 2750. 260KB 7.00
#> 3 subset(dat, x > 500) 519µs 589µs 1654. 494KB 6.74By default the summary uses absolute measures, however relative results can be obtained by using relative = TRUE in your call to bench::mark() or calling summary(relative = TRUE) on the results.
summary(bnch, relative = TRUE)
#> # A tibble: 3 x 6
#> expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
#> <bch:expr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 dat[dat$x > 500, ] 1.44 1.32 1.26 1.45 1
#> 2 dat[which(dat$x > 500), ] 1 1 1.66 1 1.05
#> 3 subset(dat, x > 500) 1.83 1.66 1 1.90 1.02bench::press()bench::press() is used to run benchmarks against a grid of parameters. Provide setup and benchmarking code as a single unnamed argument then define sets of values as named arguments. The full combination of values will be expanded and the benchmarks are then pressed together in the result. This allows you to benchmark a set of expressions across a wide variety of input sizes, perform replications and other useful tasks.
set.seed(42)
create_df <- function(rows, cols) {
as.data.frame(setNames(
replicate(cols, runif(rows, 1, 100), simplify = FALSE),
rep_len(c("x", letters), cols)))
}
results <- bench::press(
rows = c(1000, 10000),
cols = c(2, 10),
{
dat <- create_df(rows, cols)
bench::mark(
min_iterations = 100,
bracket = dat[dat$x > 500, ],
which = dat[which(dat$x > 500), ],
subset = subset(dat, x > 500)
)
}
)
#> Running with:
#> rows cols
#> 1 1000 2
#> 2 10000 2
#> 3 1000 10
#> 4 10000 10
results
#> # A tibble: 12 x 8
#> expression rows cols min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
#> <bch:expr> <dbl> <dbl> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
#> 1 bracket 1000 2 35µs 40.6µs 23255. 15.84KB 14.0
#> 2 which 1000 2 34.2µs 38µs 25354. 7.91KB 15.2
#> 3 subset 1000 2 59.1µs 64.7µs 14979. 27.7KB 13.1
#> 4 bracket 10000 2 75.3µs 95.2µs 10183. 156.46KB 30.0
#> 5 which 10000 2 63.1µs 79.2µs 12247. 78.23KB 18.6
#> 6 subset 10000 2 140.1µs 197.4µs 4925. 273.79KB 25.0
#> 7 bracket 1000 10 80.1µs 91µs 10447. 47.52KB 17.7
#> 8 which 1000 10 69.5µs 83.7µs 11339. 7.91KB 21.9
#> 9 subset 1000 10 106µs 123µs 7418. 59.38KB 15.1
#> 10 bracket 10000 10 195.9µs 229.1µs 4123. 469.4KB 38.4
#> 11 which 10000 10 108.7µs 131.2µs 7059. 78.23KB 10.9
#> 12 subset 10000 10 302.6µs 344.1µs 2780. 586.73KB 33.4ggplot2::autoplot() can be used to generate an informative default plot. This plot is colored by gc level (0, 1, or 2) and faceted by parameters (if any). By default it generates a beeswarm plot, however you can also specify other plot types (jitter, ridge, boxplot, violin). See ?autoplot.bench_mark for full details.
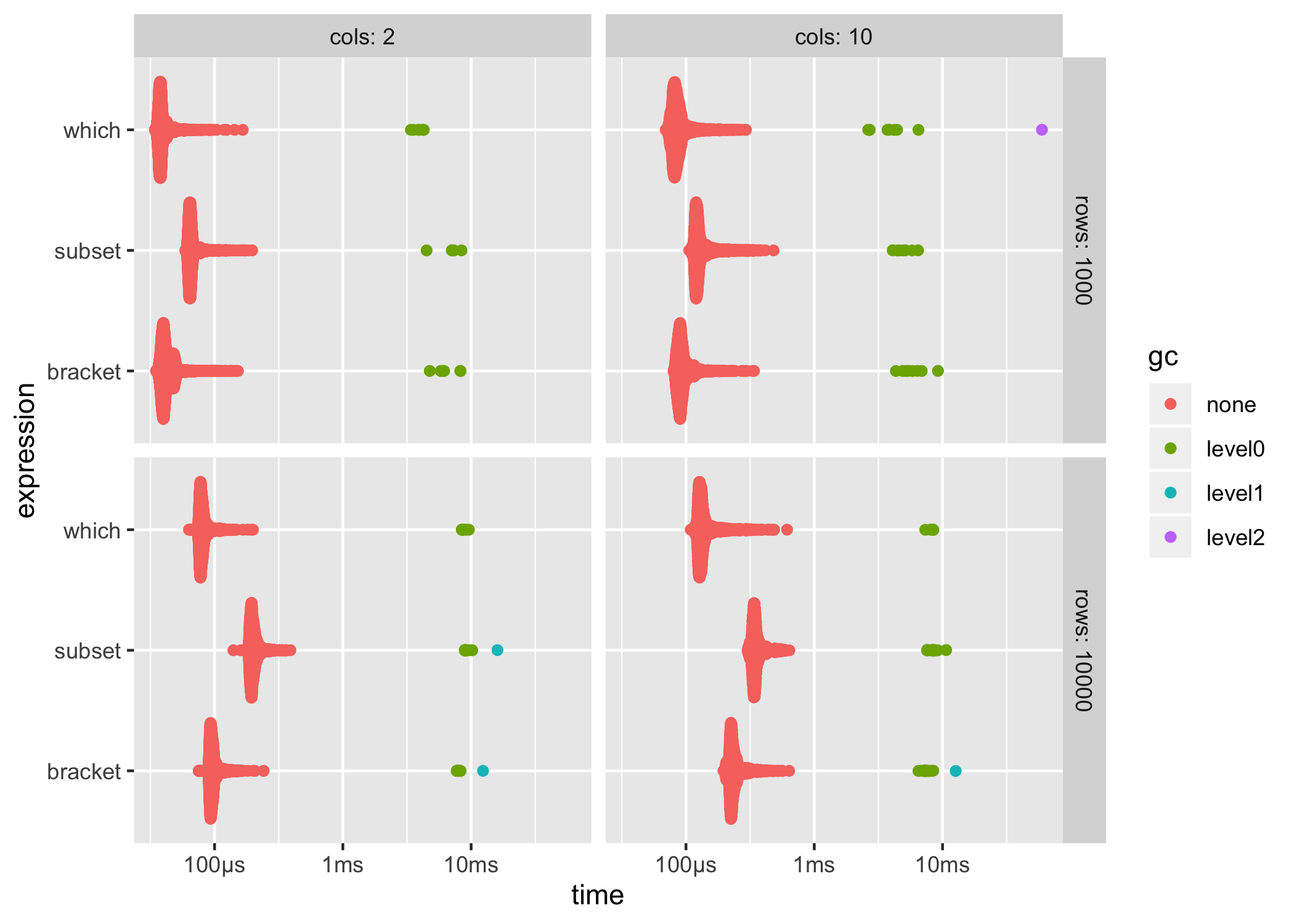
You can also produce fully custom plots by un-nesting the results and working with the data directly.
system_time()bench also includes system_time(), a higher precision alternative to system.time().
bench::system_time({ i <- 1; while(i < 1e7) i <- i + 1 })
#> process real
#> 296ms 296ms
bench::system_time(Sys.sleep(.5))
#> process real
#> 97µs 503ms