
The Project Gutenberg EBook of The Book of the Otter, by Richard Clapham
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most
other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions
whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of
the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at
www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have
to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook.
Title: The Book of the Otter
A manual for sportsmen and naturalists
Author: Richard Clapham
Commentator: William Thompson
Illustrator: F. Lees
Alfred Taylor
Release Date: May 15, 2016 [EBook #52071]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE BOOK OF THE OTTER ***
Produced by Tom Cosmas and The Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was
produced from images generously made available by The
Internet Archive)

THE BOOK OF THE OTTER
THE BOOK OF
THE OTTER
A MANUAL FOR SPORTSMEN AND
NATURALISTS
BY
RICHARD CLAPHAM
AUTHOR OF
"FOX-HUNTING ON THE LAKELAND FELLS,"
"ROUGH SHOOTING," ETC.
With Illustrations from Photographs by the Author
F. Lees and Alfred Taylor
AND AN INTRODUCTION BY
WILLIAM THOMPSON, M.O.H.

HEATH CRANTON, LIMITED
6 FLEET LANE, LONDON, E.C.4.
In these days otter-hunting is a popular sport, and in consequence there are now many more packs of otterhounds than was formerly the case. Of all beasts of chase in this country, the otter is the one about which we know least, for he is a great wanderer, a creature of the night, and therefore difficult to study systematically.
Of the many people who follow hounds, comparatively few understand the science of hunting, or the habits of the creature which forms their quarry. This is probably to some extent due to the fact that there are very few books dealing exclusively with the otter and his hunting. A knowledge of the science of hunting and the habits of the quarry can be picked up by those who have leisure to study the subject afield, but there are others whose « 8 » opportunities of doing so are limited. It is, therefore, in the hope of interesting and perhaps instructing the latter, that we have written the following chapters.
R. CLAPHAM.
Troutbeck,
Windermere.
April, 1922.
| CHAP. | PAGE | |
| PREFACE | 7 | |
| INTRODUCTION | 13 | |
| I. | THE NATURAL HISTORY OF THE OTTER | 21 |
| II. | THE OTTER'S HAUNTS AND HABITS | 42 |
| III. | OTTER-HUNTING, PAST AND PRESENT | 73 |
| IV. | HOUNDS AND TERRIERS | 112 |
| V. | REMINISCENCES | 132 |
| INDEX | 157 | |
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
| OTTER BASKING IN SHALLOW WATER | Frontispiece |
| To face page | |
| OTTER TRACKS LEAVING WATER, WALKING | 40 |
| FURROW MADE BY OTTER IN DEEP SNOW | 40 |
| TUNNEL MADE BY OTTER IN SNOW | 53 |
| OTTER TRACKS IN SNOW, JUMPING | 53 |
| THE HUNTSMAN BRINGING HIS OTTER ASHORE | 79 |
| K. AND D.O.H. RETURNING TO THE MAIN RIVER | 79 |
| A KILL WITH THE K. AND D.O.H. | 102 |
| HI, WORRY, WORRY! | 102 |
| A FAMOUS OTTERHOUND, MR W. THOMPSON'S "SNOWDROP" | 116 |
| SOME OF MR W. THOMPSON'S ROUGH OTTERHOUNDS | 116 |
| K. AND D.O.H. MOVING OFF TO DRAW | 139 |
| GOING TO THE MEET BY FERRY ON LAKE WINDERMERE | 139 |
Beck House,
Giggleswick,
Feb. 12th, 1922.
My Dear Clapham,—I am much flattered at your invitation to write an introduction to your "Book of the Otter," and only wish I were a good enough hand with the pen to do your most interesting book the justice it deserves.
If I were asked to find fault with your work I should say its only failing was its brevity. And I would ask for a few more hunts and to have them rather more elaborated. And if you could not only expound to whips, either amateur or professional, how you do your own work as such but make them into whips as good as yourself thereby you would take an enormous amount of « 14 » worry and responsibility off many a huntsman's shoulders.
As you say in your letter to me, a book on such an interesting subject is sure to create a friendly criticism, more particularly on such controversial subjects as early meets versus late ones and pure-bred otterhounds versus draft foxhounds.
Admittedly you and I have always taken rather opposite views on these two questions, so despite the very fair pros and cons you give these respective arguments in your book, may I put in a further argument in each case on behalf of hounds?
Take early meets with a pack hunting three and four days a week. It is only possible to have early meets in the hottest part of the year—say middle of June to end of August in our North Country, and a rather longer period with South and West Country packs. Say hounds meet at five a.m. on four days in the week. Hounds may have to take anything from one to two hours to « 15 » get from kennels to the meet. The men are in kennel at least an hour before the hunting pack turns out, so we know that hounds get no rest after that hour, which is probably shortly after two a.m. Hounds would normally be back in kennel after a day of this sort within an hour or two of midday. For the rest of that day, apart from the disturbance—to hounds—of ordinary kennel routine, they are unable to get genuine rest on a hot summer's afternoon. The result is that after a fortnight, or even a week of such work—and I have many instances in my old hunting diaries of both—you get a jaded pack, a tired staff, and a weary Master. And I have been unfortunate enough myself to have never seen even a hunt before eight a.m.
If anyone will guarantee to put hounds on to the line of a travelling dog otter on a given day I would be there with hounds every time. But otherwise, no thank you.
As to otterhounds versus foxhounds, I am convinced that finance, or rather the lack of it, is « 16 » the only reason why draft foxhounds are preferred to otterhounds. Otter-hunting is a poor man's sport, and few people realise what it costs to run a pack and country. If you get a Master to take a country he has very often spent enough out of his own pocket when he has paid the difference between the subscription list and the hunting expenses. And breeding hounds on a big scale adds enormously to expenses. The result is that in nine cases out of ten the pack is made up of draft dog foxhounds, and a very few rough-coated otterhounds. An attempt may be made to breed a litter or two a year from the rough otterhound bitches. Five or six puppies may be got out to walk, and three or four left in kennel. As many of these as survive—possibly two and a half or three couple—are brought on the following season, and unless they are hopeless physical wrecks they are put into the pack to keep up the theory that they are a pack of otterhounds. And good or bad workers they are often kept on for this same purpose only. Under these circumstances, « 17 » and they are far from uncommon, no wonder the average member of an otter-hunting field prefers the foxhound. Any M.O.H. can get draft foxhounds, and frequently get them as a gift—hounds that have been the best of fox-hunters and fox-catchers, but have got too slow or for any of a dozen other reasons are unable to run up to the pace of a modern foxhound pack. These draft hounds know all about hunting, and only want entering to their new quarry to make most excellent otter-hunting hounds at a minimum of expense and trouble.
But if an M.O.H. breeds otterhounds on the same lines that foxhounds are bred, breeds by selection, breeds each year enough puppies to get a big enough young entry the following year—big enough not only to be able to put down immediately any physical crock that may come in, but big enough to allow for drafting a certain number—during and at the end of their first season you can have, in my humble opinion, a pack of pure-bred otterhounds, not only not « 18 » inferior to, but superior to any pack of draft foxhounds. I may appear too enthusiastic on this point—I am certainly rather disappointed. I bought my first otterhounds in 1903. I started breeding in 1905. In July, 1914, having for two or three years prior to that date put over fifty puppies out to walk each year, I had just over forty couple of pure-breed otterhounds in kennel. And I was hoping to prove that before many more years passed my confidence in the otterhound was not misplaced. But in 1919 I was reduced to under ten couple, and circumstances have since prevented me continuing my experiment to anything like the same extent. And I must say that I have never found the otterhound quarrelsome either in kennel or out.
I hope you will forgive my keen advocacy on behalf of the pure-bred otterhound. I am sure we should both dislike to see him entirely eliminated from the hunting-field, and only to be found as a weird and useless animal on the show bench.
May your book have the great success that it deserves. That it will give great pleasure to all who know anything about the otter and the hunting of it, I am sure. That it will be the means of attracting many new converts I devoutly hope. And if I may add a wish with a yet more personal note, may I meet yourself and all my other good otter-hunting friends at many another good hunt, whether the meet be late or early, the hounds otterhounds or foxhounds.
Yours very sincerely,
W. Thompson.
CHAPTER I
THE NATURAL HISTORY OF THE OTTER
The common otter of the British Islands, known in scientific classification as Lutra vulgaris, belongs to the Mustelidę, or in other words the weasel family. Included in the latter are the martens and their allies, whose chief attributes are activity, length of body and tail, shortness of legs, widely separated toes, and small claws. The otter is the possessor of similar attributes, with additional developments to fit it for an aquatic existence. If therefore we describe the otter as an aquatic marten, living chiefly on a fish diet, we shall probably not be deviating very far from the truth. Swimming is an inherited instinct handed down through the ages, and though it has been lost by man, it has been developed and taken advantage of by many « 22 » creatures, in order to enable them to lead an aquatic existence. The reason for this intensive development of their swimming powers by certain animals probably lies in the fact that aquatic life opened a wider and safer field for them, both in the matter of food supplies and protection from their natural enemies.
The otter family is widely distributed over the globe, so before entering upon a detailed description of our British otter, it may be of interest to glance at other species inhabiting foreign countries. The typical otters are marine as well as aquatic in their habits, many of them visiting the sea, where they live in the caves and other retreats along the coast. There is one of the family, however, i.e., the sea-otter, which is entirely marine. The skin of this otter has always been keenly sought for by fur-traders and trappers, and it is owing to constant harassing by such people that the sea-otter is now all but extinct. This otter differs in many ways from its aquatic relations. It possesses large flipper-like hind feet, a short tail, « 23 » and small, delicate forefeet. The hind paws alone are used for swimming, the delicate and sensitive forefeet being employed in locating the otter's food, consisting of mussels, crabs, and other shell-fish, which it hunts for amongst the rocks at the bottom of the sea. This otter spends its entire existence in salt water, and has been found as far as twenty miles from land.
The female usually has but a single young one, born, so it is thought, on the large beds of seaweed commonly known as kelp. Lying on her back in the sea, the mother sleeps and suckles her baby in that position.
In Africa there is a species known as the spotted-necked otter, which has shorter ears, longer toes, and more hair about its nose than the common otter. Africa also produces a large otter which has more or less given up its aquatic habits. The claws on this otter's forepaws have disappeared, while those on the hind feet have practically done so. In India there is a small otter whose claws resemble those of the foregoing, and in both « 24 » animals the sense of touch in the forepaws is extremely delicate, which no doubt enables the creatures to locate certain of their prey by feeling for it. In the large African otter the webs between the toes are greatly reduced, and the facial bristles or "whiskers" are much softer than those possessed by the common otter.
South America can boast of a very large otter, whose tail is wider and more flattened than is the case with the otters above mentioned. It will thus be seen that there are only slight differences between individuals composing the typical otters.
 Otter's Rudder.
Otter's Rudder.The common British otter (Lutra vulgaris) is known by a variety of names in this country. The Welsh call the animal dwrgi, while in Cornish it is written durgi. In the Highlands, where Gaelic is spoken, the name is dņbhran. The physical formation of the otter is admirably adapted to fit it for an aquatic existence. In order to offer the least possible resistance to the water when the animal is swimming below the surface, the otter's head and muzzle are flattened, and the ears are « 25 » very small. Both ears and nostrils can be closed to exclude the water. The body is long, low, and sinuous in movement, set upon short legs which are loosely articulated. The feet are palmate, with five toes armed with short, non-retractile claws, and perfect interdigital webs. The tail is more than half the length of the head and body, broad at the base, and horizontally flattened. Beneath the root of the tail will be found a pair of small glands containing a fetid liquid secretion. Being an aquatic, sub-Arctic species, the otter is furnished with a body covering of two kinds. The thick, close under-fur, which attains special luxuriance of growth, is provided for two purposes, i.e., for keeping out the wet when the animal is in the water, « 26 » and for preventing loss of heat during cold weather. Overlying this under-coat is a covering of longer hairs, which are stiffer and more shiny, greyish in colour at the base, and brown at the tips. This dark colouring shows in most pronounced fashion on the upper portions of the body, and on the outer surfaces of the legs and shoulders. The inner portions of the legs, belly, chest, throat, and cheeks are brownish-grey. The throat often shows a good deal of white or greyish-white in irregular patches. This, however, varies considerably in individual specimens, some showing a good deal of it, others practically none at all. Turning again to the head, we find the eyes small and dark coloured, while the so-called "whiskers" are long, stiff, and thick at the base. These long, stiff hairs grow on the upper-lip, and there is a tuft of them over each eye, and two tufts—one below the other—on each cheek. In the case of the domestic cat these "whiskers" are soft, and possess a very delicate sense of touch, thus enabling the animal to creep noiselessly through « 27 » undergrowth in pursuit of prey. Should the cat's "whiskers" touch the grass or other growth on each side, puss is then instinctively aware that there « 28 » is not sufficient room for her body to pass, and that she will therefore make a rustling sound if she persists in her advance, and so alarm her prey. These soft hairs on the cat's face are quite adequate for her purpose, because she hunts on land and hates wet. Soaked with water the soft hairs would droop and prove useless, and so it is for this reason that the otter's "whiskers" have gradually developed until now they are strong and stiff in order to withstand the exigencies of frequent underwater journeys. They are used, too, in a rather different way, for although while on land they may aid the otter to make a quiet approach on prey, their chief purpose is for locating food—in the shape of frogs, fish, etc.—either beneath stones, or on the bottom of the riverbed. The long hairs on the otter's upper-lip are susceptible of considerable movement, for their development has been followed by that of the muscles beneath, which give the puffy appearance to the otter's face. Provided with perfect interdigital webs on all four feet, the otter when « 29 » swimming slowly, paddles in exactly the same manner as a dog. When the speed is increased, however, the tail is brought into action, being moved from side to side, while the body is thrown into sinuous curves.
 OTTER'S HEAD, SHOWING WHITE MARKINGS ABOUT THE MOUTH
AND THROAT.
OTTER'S HEAD, SHOWING WHITE MARKINGS ABOUT THE MOUTH
AND THROAT.The otter, like the seal, feeds upon fish, but whereas the seal swallows its prey whole and entire, the otter masticates its food. The teeth of the otter are therefore adapted to crushing bones, which, if not thoroughly broken up, would lodge in the animal's throat. The two back teeth in the otter's upper jaw are considerably enlarged, and are provided with cutting edges and a flat crushing surface. Provided with a short and powerful jaw, armed with a formidable array of teeth, the otter is capable of inflicting a very nasty bite, as many a hound and terrier, as well as otter-hunter, has had cause to remember. Luckily the otter is a clean-feeding animal, and the after results of a bite are usually not serious.
In the matter of size and weight, otters vary considerably, those found on or near the sea « 30 » coast being usually heavier than otters frequenting inland waters. No doubt the quantity and quality of the food supply has a good deal to do with the variation. Roughly speaking, the average weight of a dog otter is from 20 lb. to 24 lb., and of a bitch, 16 lb. to 20 lb. As far as record weights are concerned, Daniel mentions an otter taken in the river Lea in October, 1794, which scaled "upwards of 40 lb." Turning to a more reliable source of information, however, we find in the Field of July 5th, 1919, a list of the lengths and weights of eleven large otters killed in Norfolk. I take the liberty of quoting the particulars which are as follows:
Males, 48 inches, 37 lb.; 53½ inches, 30 lb.; 50½ inches, 28 lb.; 53 inches, 27 lb.; 50 inches, 27 lb.; 50 inches, 23 lb.; 48 inches, 23 lb.; 49 inches, 18½ lb.
Females, 46 inches, 16 lb.; 43 inches, 16 lb.; 44 inches, 14 lb.
It will be seen from the above how extremely weight varies in relation to measurement. Bitch « 31 » otters occasionally weigh far heavier than any of those mentioned in the foregoing list.
In the Field of September 22nd, 1917, an old record is given (March, 1813) of a large bitch otter trapped near Leven's Hall, Westmorland, measuring 54 inches, and weighing 27¾ lb. The record otter killed by hounds, a dog otter of 34 lb., was accounted for by the Essex O.H. on July 10th, 1907, during Mr Rose's mastership of that pack. This otter was found in the sea marshes near Ipswich. Generally speaking, very few otters of 30 lb. or over are accounted for by hounds.
It appears to be a matter of uncertainty as to how long a bitch otter goes with young. We have heard it said nine weeks, but have no reliable evidence to go by. As to the number of cubs in a litter, two appear to be more often laid down than three, although five have been more than once found in the same couch. Roughly speaking, the average number appears to be from two to three.
As to how many years an otter in a wild state will live, it is practically impossible to say. We have seen otters killed by hounds, whose general appearance and state of their teeth pointed to the fact that they had arrived at a ripe old age. Otter cubs of similar age have been found in every month of the year, thus exploding the old supposition that otters bred only in spring. Young bitch otters appear to pair as soon as they arrive at maturity, thus cubs are produced as above stated.
Otters of abnormal colour make their appearance from time to time. In the Badminnten volume on "Hunting," there is an account of a cream-coloured otter killed on the West Dart, while in "A Fauna of Argyll" by Harvie-Brown and Buckley, there is mention of a pure white otter which was killed in Jura.
Although a clean-feeding animal, the otter is a creature one hardly associates with human food. For all that the heart and other portions of an otter's anatomy have been served up at table on several occasions ere now, presumably we suppose « 33 » for experimental purposes. Which reminds us of the yarn concerning the old trapper, who when asked if he had ever eaten turkey-buzzard, replied "Yes, siree, I have eaten turkey-buzzard, but I don't hanker after it." On one occasion we became possessed of a dead otter, whose carcass, after skinning, we presented to two dogs. The latter promptly turned up their noses at it, whereas several cats to which it was afterwards given set about devouring it quite keenly. In the case of hounds, unless the carcass of their quarry is still warm and they are excited by the free use of horn and voice, they will show no great desire to do more than tear the body of an otter.
The otter's hide—covering a sinuous body, with loosely articulated limbs—is tough, and offers more resistance to hounds' teeth than the skin of a fox, which soon disintegrates when worried by the pack. As far as hounds are concerned, the scent of an otter must at times be to them exceedingly strong, yet to the human nose—even if the latter is held close to the animal's body—there is only a « 34 » faint and not unpleasant odour, very different to the rank scent of a fox.
As previously mentioned, there appears to be considerable uncertainty as to how long the bitch otter goes with young. In the "Master of Game," the oldest and most important work on the chase in the English language, written between the years 1406 and 1413 by Edward III.'s grandson Edward, second Duke of York, there is a short chapter on "The Otter and His Nature," in which it says that the otter bears her young as long as the ferret does. This chapter is of great interest, both as regards the knowledge of venery possessed by mediaeval hunters, and the quaint wording of the letterpress. For this reason we take the liberty of quoting it in full. It says, "An otter is a common beast enough and therefore I need not tell of his making. She liveth with (on?) fish and dwelleth by rivers and by ponds and stanks (pools). And sometimes she feedeth on grass of the meadows and hideth gladly under the roots of trees near the rivers, and goeth to her feeding as doth « 35 » other beasts to grass, but only in the new grass time, and to fish as I have said. They swimmeth in waters and rivers and sometimes diveth under the water when they will, and therefore no fish can escape them unless it be too great a one. They doth great harm specially in ponds and stanks, for a couple of otters without more shall well destroy the fish of a great pond or great stank, and therefore men hunt them. They go in their love at the time that ferrets do, so they that hold (keep) ferrets in their houses may well know the time thereof. They bear their whelps as long as the ferrets and sometimes more and sometimes less. They whelp in holes under the trees near the rivers. Men hunt at them with hounds by great mastery, as I say hereafter.[1] And also men take them at other times in rivers with small cords as men do the fox with nets and with other gins. She hath an evil biting and venomous and with her strength defendeth herself mightily from the « 36 » hounds. And when she is taken with nets unless men get to her at once she rendeth them with her teeth and delivereth herself out of them. Longer will I not make mention of her, nor of her nature, for the hunting at her is the best that men may see of her, save only that she has the foot of a goose, for she hath a little skin from one claw to another, and she hath no heel save that she hath a little lump under the foot, and men speak of the steps or the marches of the otter as men speak of the trace of the hart, and his fumes (excrements) tredeles or spraints. The otter dwelleth but little in one place, for where she goeth the fish be sore afraid. Sometimes she will swim upwards and downwards seeking the fish a mile or two unless it be in a stank.
[1] The author of "Master of Game" does not say anything more about the otter.
"Of the remnant of his nature I refer to Milbourne[2] the king's otter-hunter."
[2] The Milbourne referred to by the Duke of York can scarcely be any other than the William Melbourne we find mentioned in Henry IV's reign as "Valet of our Otterhounds" (note in appendix to "Master of Game").
If otters "bear their whelps as long as the « 37 » ferrets," the period of gestation is six weeks or forty-five days. Bitch ferrets come in heat in April or May, and unless mated some of them apparently remain more or less in that condition during the summer months.
The excrement of the otter, known in hunting parlance as "spraints," "wedging," or "coke," is usually of a blackish colour, and contains the bones and scales of fish. Sometimes it shows the remains of fur or feather, which is proof positive that the otter does not live entirely upon a fish diet.
Where an otter has been feeding on frogs, the coke is usually a yellowish colour. In sand or soft earth an otter will scrape the latter into a small mound, like a cat, and for the same purpose.
Coke is generally found on stones in midstream, or at points where the otter enters or leaves the water. A small grassy promontory is a favourite place, and at such spots the grass often grows particularly green. If the grass is long, the coke will be found hidden amongst it. It is popularly supposed that the direction in which an otter is « 38 » travelling—up or down stream—can be verified by the position in which the coke is left on the stones. In our experience there is little reliability about this theory. On a rock in midstream the position of the coke is quite as likely to be in the centre as at the sides, particularly if there is a tuft of grass or other growth on the stone.
An otter is quite likely to turn round, just as a cat or dog does, prior to depositing the coke, therefore the position of the latter can hardly be a reliable guide as to the direction taken by the animal when it eventually moves off.
Owing to being the possessor of a webbed foot, with five toes and short claws, the otter leaves a track—in hunting parlance "spur," "seal," or "mark,"—entirely different from that of any other animal to be met with in this country. Amongst the general literature relating to the otter, we have found small reference to the animal's footprints, while in some cases the information on the subject was incorrect. For instance in one article we read, it states "No other creature, saving a cat, « 39 » leaves such a print on Nature's page as does an otter. Four round small toes and, if the soil be favourable, a plain triangle just behind where the webbing of the foot has rested."
No. 3. |
No. 4. |
Now an otter—like the badger, stoat, weasel, and hedgehog—has five toes on each foot, and the marks of the claws or nails are always visible in the footprints. A cat has four toes, armed with « 40 » retractile claws, the marks of which are not shown on the ground, except when the animal is about to make a spring. Although a cat track may approximate in size to that of an otter cub, the latter always shows claw-marks, and partial if not entire imprints of five toes. On hard ground, claw-marks will show when the impression of the rest of the foot is practically invisible, so anyone with a knowledge of woodcraft can hardly mistake the track of a cat for that of an otter cub. In the same way with the footprints of hounds, terriers, or other dogs, their tracks all show the imprints of four toes, plus the marks of the claws. A terrier's track is far more like that of a fox than an otter, while hounds leave large footprints, easy to distinguish.

Otter Tracks Leaving Water, Walking.
(Photo by R. Clapham).
|

Furrow made by Otter in Deep Snow.
(Photo by R. Clapham).
To face p. 40.
|
We have also seen it stated that the track of an otter is "recognisable by the mark of its five toes, and the absence of a heel." Under certain conditions this is true enough, but on favourable ground the mark of the heel is plainly visible. In like manner an impression of the webbing is sometimes left. In snow of fair depth, the individual tracks of an otter are more or less obliterated by the drag of the animal's body, which leaves a furrow as if a miniature snow-plough had been at work. Also in snow the drag of the otter's tail—in hunting parlance "rudder" or "pole"—is generally to be seen.
The otter has three gaits: walking, jumping, and galloping. The walk shows a line—usually rather twisting—of footprints one behind the other. When jumping the tracks appear in pairs, with an interval between each pair. At this gait the imprints of the hind feet cover the tracks made by the forefeet. At the gallop, which is really jumping at top speed, the hind feet are thrown ahead of the forefeet.
CHAPTER II
THE OTTER'S HAUNTS AND HABITS
As mentioned in the previous chapter, otter cubs may be born in any month of the year. Prior to laying down her young, the bitch otter selects a couch in the vicinity of good feeding ground. Her choice of a retreat will vary with the locality in which she happens to be at the time. In the low country her cubs may be laid down in a dry drain in the meadows, where frogs are plentiful, and the ditches contain a supply of eels, or amongst the brushwood in some large covert, where the ground is swampy, and through which one or two small runners meander on their way to join the parent stream. In the north, where the rivers are swift and rocky, the cubs may first see the light of day in some cairn or pile of boulders, situated high « 43 » up near the source of the stream, or in some rocky earth adjacent to a mountain tarn. On the grouse moor they may be found in some sod drain or other hiding-place amongst the peat and heather, near a pool or pools containing fish, and frequented by wildfowl as well as frogs and such small deer.
Quite small cubs are often found in holts in the bank of a main river, but it is pretty safe to say that the majority of bitch otters move up-stream, either to the head-waters, or up some side-runner prior to laying down their cubs. The latter have on various occasions been discovered actually beneath, or in close proximity to human habitations.
In the Field of October 29th, 1921, there is an interesting description of such an occurrence, which we take the liberty of quoting. It says: "An odd experience is recorded to have happened in the year 1790 to Mr William Bethel, the then owner of Watton, and a guest. He and a clergyman were sitting quietly at dinner, when they were surprised by an extraordinary noise beneath the dining-table for which they could not account, and « 44 » at length they were so much annoyed by it that they sent for a workman to take up the floor, when to their great astonishment they found that an otter which had inhabited the moat had established her nest beneath the boards of the floor, and had there deposited her litter of young ones, by whose uncouth cries it was that the dinner-party had been disturbed."
In The Gamekeeper for May, 1914, there is another interesting account of a somewhat similar nature. It says: "On March 13th last, Mr Colwill, a tenant on the Trebartha Estate, Cornwall, lost a lamb, and there being a mouth of a large drain in the field, thought perhaps there might be a chance of the lamb having gone up the drain. Getting a long stick he put it up the drain, and feeling something move he thought it must be the lamb, but on turning round, saw the lamb coming up the field towards him. The same evening he put some lambs in the shippen in front of some cows, putting them on some hay. Before going to bed he went to see that the lambs were « 45 » all right. He was just hanging up his lamp, when something—he could not see what—rushed out past him. When he went to look at his lamb, he found a young otter lying with the lamb."
The account goes on to say that on the particular night in question, the local rivers were in flood. The above seems to point to the fact that the bitch otter had been flooded out of the drain, and had carried her cub to the shelter of the shippen. A photograph of the lamb and the otter cub was reproduced in conjunction with the above letterpress.
Otter cubs, like young foxes, are born blind. Fox cubs remain so for a period of about three weeks, and it is probable that a similar length of time, or perhaps rather more, elapses ere young otters can see. In the Field of November 26th, 1921, there is an account of an otter cub whose mother was inadvertently killed by hounds. This cub was rescued and brought up by hand. When taken from the holt its age was estimated at fourteen days. Sixteen days later the cub opened « 46 » its eyes, thus a period of thirty days elapsed from the time of its birth until it could see. At the end of the thirty days the cub weighed 14 ounces. It was at first fed on milk and water, but became very thin on this diet, so a change was made to "Mellins" as mixed for a new-born child. On this the cub thrived, its weight on October 11th being just under 2 lb. It was taken from the holt on August 20th. Had this cub been fed in the ordinary way by its mother it would possibly have opened its eyes at a rather earlier date, as it would have escaped the set-back caused by an unsuitable diet. The eyes of the adult otter are very dark coloured, but those of a cub are at first much lighter, not unlike the eyes of a young fox cub.
When the cubs are able to travel, the bitch otter leads them down from the head-waters to the larger streams. The cubs remain with their mother for some considerable time, as witness the constant occurrence of cubs of from 10 lb. to 12 lb. being put down in company with the bitch. They consort with their mother until she goes off to rear « 47 » another family, when they are then left to fend for themselves. From this it is apparent that the otter has but one litter per year.
There is a great deal yet to be learnt about the otter, for, being more or less a creature of the night, and elusive in its movements, it is extremely difficult to study systematically. Otter cubs, although somewhat delicate, are not difficult to hand-rear, and make very interesting and tractable pets. If healthy to start with, cows' milk diluted with water is at first a satisfactory diet. Both cubs and adult otters are of course easy enough to study in captivity, but like many other creatures confined under similar conditions, they soon exhibit certain abnormal tastes and habits, and therefore afford little or no real clue to their behaviour in their natural habitat. At the Zoological Gardens in London, the otters will eat almost anything thrown to them by visitors.
The bitch otter shows great affection for her young, and will hang about in their vicinity in the face of hounds or human intruders. If a bitch « 48 » with cubs is killed, the cubs, if well grown, will search the vicinity for their parent, the same applying to one of a pair which has been caught in a trap, its mate remaining near it all night in an attempt to get it away. On these occasions the otters make a considerable noise, blowing and snorting in their agitation. On one occasion some years ago, a brother of ours found three small otter cubs on a Yorkshire beck, which he eventually captured. The bitch otter remained close at hand, making a great fuss, regardless of any possible danger to herself. The cubs were carried home, a distance of a mile or more, but were returned within a short time to the pool where they were found. The bitch otter again made her appearance, and eventually went off with her restored family.
Otters, being great nomads, wander long distances up and down our rivers, frequently crossing high watersheds, and travelling far across country. Having no fixed abode like the fox, the otter inhabits temporary retreats or holts during « 49 » the course of his journeyings. Most of these holts have been used by generations of otters, and many a drain or other shelter long forgotten by the people of the neighbourhood is still regularly inhabited by Lutra and his kind. A holt may consist of a tree-root on the river-bank, a dry drain, or a wet one containing a dry lying place, a stick-heap near the stream, or situated in a plantation at some distance from the water. On the rocky rivers of the North, many of the holts consist of piled-up boulders on the hill-side, most of which are at some distance from the nearest beck or tarn. These rock-holts, many of which lie at a high altitude, are occupied by otters when crossing from stream to stream over a watershed. In summer, otters frequently "lie rough," or in other words spend the day above ground. Near a lake or tarn an otter will often curl up in the rushes or long grass at the water's edge. If disturbed he will then slide quietly into the pool, and unless hunted by hounds, will not show himself again. Sometimes he will lie on a bank or in a hedge close « 50 » to the mouth of a drain, the latter serving him as a safe retreat when danger threatens. In fact, during the warm weather, otters are found lying rough in all sorts of unexpected places, often to the great surprise of those who fondly imagine that the animals never leave the vicinity of water.
Certain tree-roots and also rock-holts have their entrances under water. In some of them there cannot be any great amount of ventilation. An otter cannot live without air, yet presumably it can exist with less than most creatures. Otter cubs are sometimes laid down in holts of the above nature, where there is no ventilation shaft, and we have heard the theory expressed that under such conditions practically all the fresh air that the cubs get is carried in to them in their mother's coat. In our experience, however, even though a holt has an underwater entrance, there are usually plenty of air passages coming down from above, at any rate, sufficient to supply a more than adequate amount of fresh air for breathing purposes. The advantage of an underwater « 51 » entrance to an otter lies in the fact that he can get in and out without showing himself, and once inside he may be "out of mark," or in other words, his scent is not carried to the outer air, so that if hounds come along they cannot wind him in his retreat.
After his night's peregrinations, an otter will return to his holt, but prior to settling down in his chosen retreat, he often visits one or two other tree-roots on the river-bank. Hounds sometimes mark at these places, only to find that their otter has gone on.
Along the sea coast, otters inhabit the water-worn caves and other retreats about the cliffs. Wherever there is an open boathouse on lake or river, otters are pretty sure to resort to it. We have examined many such places, and almost invariably found otter coke lying about on the planking, and sometimes actually in a boat or boats. In bad weather a boathouse affords a dry lying spot, and no doubt this is why otters visit it.
In order to thoroughly realise the wanderings « 52 » and often long cross-country journeys undertaken by otters, one must track them in the snow. On one occasion such a trail led us for a good ten miles overland, the otter having left a stream, and made his way uphill via a small runner. The latter petered out in the open ground, but the trail led on in the direction of a frozen reservoir. Round this the otter had gone, then he followed the stream from the outlet for some distance, after which he turned straight across country. Three or four big stone walls had then intervened, but the otter—which had probably been over the same route before—made straight to certain smoots, and passed through with no unnecessary searching for a way out. He then visited a small lake, also frozen, and again took to the outlet stream, down which he went until he arrived at the main river. It must have been a pretty hard trip for so short-legged an animal, for the otter left a furrow in the snow which was quite deep. From the point where he left the stream where we picked up his tracks, to the spot where the trail entered the main river in the next dale across the watershed, the otter had not stopped once, but had kept toddling on. In the Lake District, otters regularly travel the passes over the hills, visiting the mountain tarns, and going from one dale to another.

Tunnel Made by Otter in Snow.
(Photo by R. Clapham).
|

Otter Tracks in Snow, Jumping.
(Photo by R. Clapham).
To face p. 53.
|
Otters are playful beasts, a favourite game of theirs being sliding. They choose a steep clay bank, or a smooth snow slope, and toboggan down it on their stomachs with evident enjoyment. Although one seldom sees these slides in this country, they are very common in Canada where we have often come across them. During the cold weather of a Canadian winter, otters spend a good deal of their time beneath the ice, being able to breathe at the air-spaces round the shore. These air-spaces are left when the water lowers after the ice is formed.
Concerning the otter's feeding habits, there appears to be a good deal of misconception. Some people imagine that the otter exists entirely on fish, and for this reason should be done to death as a river-poacher at every opportunity. We « 54 » have in the previous chapter compared the teeth of the otter and the seal, the latter animal swallowing its food whole, while the former masticates its food. Seals live upon fish, but it must be remembered that the otter belongs to the marten family, and, though well adapted to lead an aquatic existence, it still retains some of the marten's hunting instincts, and its teeth are suited to seizing and holding both furred and feathered prey. The pine marten, stoat, and weasel will all eat trout greedily when they can get it, so it is only natural that the otter, their relation, well equipped for swimming and water work, should show the same taste. As a matter of fact he does exhibit the same taste as his smaller relatives, and to a much greater degree, but he is also glad to vary his diet and add both flesh and fowl to the menu.
The uninitiated, whose knowledge of otters has been gained by visits to the Zoological Gardens, while realising the swimming ability of the animals, look upon them as clumsy beasts on land, and ill-adapted to lead an active existence on terra firma. « 55 » In an article comparing the badger and the otter, it says, "The otter, on the other hand, though an expert swimmer, is on land nearly as clumsy as his cousin the badger." The author of the said article can have done little or no otter-hunting, for if he had, he would never have made such a foolish statement. Despite his webbed feet, the otter is built like the weasels, and exhibits a great deal of their activity and quickness on land. For this reason he is well able to cope with furred and feathered quarry.
Beginning the otter's menu with fish, we find he eats salmon, sea trout, trout, and coarse fish. On the west of Scotland and in the Hebrides, otters live a good deal on the coast, but in the autumn they follow the salmon up the streams. Where salmon are plentiful and easily secured, otters kill a fish, take it ashore, and eat a portion of the shoulder only. In the old days in the Highlands, when otters were more numerous than they are at present, the crofters used regularly to visit the otters' landing places, in order to gather the salmon « 56 » left there. The marks on such fish were known as the "otter's bite." In that delightful book, "Wild Sports of the Highlands" by Charles St John, the author refers to the above practice as follows: "I was rather amused at an old woman living at Sluie, on the Findhorn, who, complaining of the hardness of the present times, when 'a puir body couldna' get a drop smuggled whisky, or shot a rae without his lordship's sportsman finding it out,' added to her list of grievances that even the otters were nearly all gone, 'puir beasties.' 'Well, but what good could the otters do you?' I asked her. 'Good, your honour? Why scarcely a morn came but they left a bonny grilse on the scarp down yonder, and the vennison was none the waur of the bit, the puir beasts eat themselves.' The people here call every eatable animal, fish, flesh, or fowl, venison, or as they pronounce it 'vennison.' For instance they tell you that the snipes are 'good vennison,' or that the trout are not good 'vennison' in the winter."
Although an otter is a capable swimmer, he cannot « 57 » travel half as fast as a salmon under water. In low water a single otter can tire out or corner a salmon in a pool, but evidence leads us to believe that otters often work together, one driving the salmon about, while the other keeps watch on the shallows. On all rivers there are places where fish can be more or less cornered when the water is at normal level, and of course when it is very low in time of drought, salmon and other fish are practically pool-bound, and thus fall victims to otters and other predaceous creatures. It is pretty safe to say that an otter—like a pike, or a cannibal trout—will go for any fish which appears to be weak or in difficulty. A spinning lure—such as a spoon that wobbles instead of turning truly—is often far more attractive than one that spins "like a streak of silver."
In the Field of June 5th, 1920, there is an account of an otter attacking a hooked salmon. The writer of the account says, "While I was playing a salmon on the Teify on Friday, May 21st, an otter made two attempts to get at him, and « 58 » very nearly succeeded once. This seems so unusual to me that it would be of great interest if others have had a similar experience. This incident took place about eight in the evening, and in a pool where there was only an opening of a few feet where one could gaff the fish owing to trees. The trees undoubtedly accounted for the otter failing to see me, but as soon as he raised his head above water in midstream and saw that there were others as well as himself after that fish he soon cleared off, and the fish was successfully landed. The wild rushes made by the salmon after the otter's first attempt were extraordinary, as the fish was about done and fit for gaffing. To me this was a clear proof of the instinctive fear and wonderful vitality in a fish when his natural enemy appeared."
Other instances of a similar nature have been recorded from time to time, in some of which the otter has succeeded in taking the hooked fish. There is no doubt that an otter or otters frighten fish, particularly salmon, when chasing them about a pool. The instinct of all wild animals is to « 59 » attack a weakly or wounded creature, even if belonging to their own kind, and the otter which goes for a hooked salmon does so because he knows he stands a better chance of catching it than other fish in the same pool which are free and untrammelled.
The otter must, therefore, do considerable good by ridding the streams of weak and sickly fish. An otter deals with large sea trout as it does with salmon, but in the case of trout it frequently eats them entire, leaving nothing to waste. When devouring fish an otter eats like a cat, with half-closed eyes. In the case of coarse fish, the otter often discards the head and tail, and in the same way with an eel, the head may be left. Those who decry the otter as a fish-poacher should remember that the animal does not confine his attentions solely to one pool or to one species of diet during his nightly wanderings. He may fish and otherwise feed up-stream for some miles, taking a trout here, an eel there, and perhaps a young rabbit somewhere else.
We have already seen that the otter must do good by killing sickly or wounded salmon, and in the same way with trout, he captures many an old cannibal fish which is far better out of the water. These old trout not only prey on their own smaller relations, but are great devourers of fish spawn, and the same applies, only in a much greater degree, to eels, which are the worst vermin in or about a river or lake. Many coarse fish, too, are inimical to spawn and young fry, therefore the otter does far more good than harm by feeding on them. Eels and frogs, the latter being skinned by an otter, are the first quarry that the bitch otter teaches her cubs to hunt. These are sought for on land and in the wet ditches and shallow runners. Later, the cubs are initiated in the art of fishing.
When first introduced to water, the cubs show considerable reluctance to swim. This can hardly be because they are unable to do so, but rather owing to a youthful aversion—as in the case of a puppy—to entering a strange element for the first time. The bitch therefore takes them to a stone « 61 » in midstream, and either pushes them in, or leaves them there until they are at last tempted to enter the water and follow her. On the sea coast otters spend a good deal of time searching for flounders in the shallow pools. They also eat crabs, lobsters, sea anemones, and various crustaceans. Otters sometimes visit the lobster fishers' creels, and there are instances on record of partially grown otters having been found drowned in the creels. On inland lakes and streams otters feed on fresh-water mussels and cray-fish.
As previously mentioned, it is no uncommon thing to find the remains of fur and feather in otter coke. Otters capture waterhens and dabchicks, although we are of the opinion that they prefer other food if they can get it. At any rate we are familiar with a certain reed-fringed pond on the hills, where a bitch otter and two cubs of about 12 lb. weight resided for some months. This pond was also occupied by quite a number of waterhens, yet there were no apparent remains of these birds to be found in the vicinity, which « 62 » pointed to the fact that the otters left them pretty much alone.
A rather curious thing happened when we visited the pond with hounds. At first the waterhens were much in evidence, but after hounds had been at work for an hour or two, we began to find dead waterhens lying about. These were not killed by hounds, but were drowned, and had practically—as far as we could see—committed suicide. To escape danger a waterhen will keep diving, and the birds under discussion had evidently—owing to the continual presence of hounds—done so until they were tired out, and subsequently perished under water. What made their behaviour stranger still was the fact that there was a small covert adjoining the pond, in which the birds could have found sanctuary on terra firma until all danger was past.
Both dabchicks and waterhens devour fish spawn, so otters do good by thinning out the ranks of these birds. At times otters will take game-birds, and there are authentic records of grouse, « 63 » pheasants, and duck having been killed by them. One or two instances of this will suffice. In "The Natural History of Sport in Scotland," by Tom Speedy, the latter says: "That he can scent and pounce upon his prey like a fox was demonstrated by following his tracks among snow up Corrie Macshee Burn at Dalnaspidal. The trail left the water-side and showed where the animal had made a bound and caught a grouse in its roosting-place among the snow. Returning to the stream, he had crossed on to a boulder in the centre of the burn, where he devoured part of his prey." The same author mentions a case of an otter on the Biel estate in East Lothian, which dragged a foster-mother hen out of a coop and partly devoured it, as well as a number of young pheasants big enough to sit out amongst the grass. Traps were set, baited with the dead bodies of the birds, and a large otter was secured; the massacre then ceased.
In The Gamekeeper for August, 1913, there is a note concerning the deaths of fifteen sitting pheasants in a covert beside a river. Each bird « 64 » had a hole gnawed down through the back, the carcasses being left lying near the nests, not an egg having been touched. A duck caught on her nest is treated in the same way by an otter. In The Gamekeeper for June, 1919, there is a note concerning an otter which was caught in a tunnel-trap baited with rabbit paunch. The trap was set in the middle of a one hundred acre wood. The otter was a cub, weighing 9½ lb.
Waterhens and dabchicks, particularly the latter, when taken by otters, are pulled under the water, though they may be captured amongst the reeds and other undergrowth as well. Ducklings sometimes fall victims to the otter, though as a rule big pike do the greatest harm in this direction. Pike have been known to take pheasants as well as duck which had fallen into a lake during the course of a shoot. From available evidence, otters on a stream containing trout and coarse fish seem to prefer the latter. Possibly they are easier to capture than trout. On hill-streams, where the fish are small but very numerous owing to shortage of « 65 » food, otters must do a great deal of good by reducing the stock.
As far as furred prey is concerned, otters will kill and eat rats, water-voles, and young rabbits. We have on several occasions seen where a small bunny had been caught by an otter. On marshes where duck shooting is carried on, otters find and feed on wounded duck, exactly as do foxes. Here again they do good by acting as scavengers, as well as by putting winged birds out of their misery. Rabbits appear to be the largest four-footed creatures preyed upon by otters, but we have heard it suggested by an old Lakeland dalesman that they will on occasion take lambs. Although we bring forward this suggestion with great diffidence, it is quite possible that there is some truth in it. Our informant lived by the shore of a lake in an out-of-the-way part of the country, where at one time pine-martens were very plentiful. It is a well-known fact that martens will kill lambs, and an otter, which is a much more powerful animal, could easily do the same if so inclined. Anyway, the old « 66 » dalesman more than once found the carcass of a lamb left close to the edge of the water on the lake shore, with the tracks of otters round about it. Neither a hill-fox nor marten would be likely to drag or carry the carcass to water, and the whole thing certainly pointed to the work of otters.
An otter is a predaceous animal of the weasel family, strong, and active in its habits, and would experience no difficulty in tackling a lamb. It is never safe to be dogmatic in one's statements concerning the habits of wild creatures, because generally speaking, the only regular thing about them is their variability. Cases have occurred where otters were responsible for killing ducks, grouse, pheasants, and rabbits, and though such behaviour is only occasional on the part of the average otter, it shows what he will do when so inclined.
In winter otters are sometimes hard put to it to find food, and they have been known to take poultry at such times. In the same way regarding the dalesman's statement about lambs, an otter « 67 » may occasionally kill one, although most people would laugh at such an idea. We know that hill-foxes take lambs, having scores of times found carcasses in and about the earths, yet one meets hunting people who resolutely refuse to believe that Reynard ever falls so far from grace as to feed on lamb. A fox will eat trout when he can get it, and so will many dogs. We have one now which eats small trout as greedily as a cat, and no doubt foxes secure many fish when the hill-streams are dead low in summer. It is no more strange for a fox or a dog to eat fish than for an otter to take an occasional lamb. All three are carnivorous—the otter being least so—and when all is said and done, wild animals show very unusual traits at times.
Summing up the otter's feeding habits, we find he kills fish, and in the case of salmon he is certainly wasteful. To set against this he takes many a sickly fish, as well as cannibal trout, all of which are better out of the way. He kills waterhens and dabchicks, both devourers of fish « 68 » spawn, and he slays quantities of eels, which are the worst vermin to be found in lake or stream. Game is only an occasional item on his menu, and nobody grudges him a few young rabbits.
Otters, therefore, if kept within reasonable limits, do their share of good, and, like the fox, provide the very best of sport when hunted. When Reynard is rolled over by hounds it is the debt he pays for the privileged existence of himself and his kind, and the same thing applies to the otter. Given a good pack of hounds, hunting their district properly, otters will be kept sufficiently in check, and good sport will be enjoyed by riparian owners and others.
The only occasion on which an otter can do really extensive damage is when he gets access to a trout hatchery. Once he finds his way to the breeding ponds he will kill fish right and left. If, however, such places are properly fenced off—as they should be—they will never suffer from the attentions of otters. Swans and other wildfowl, herons, dabchicks, waterhens, kingfishers, frogs, « 69 » cannibal trout, and eels do far more damage to fish and fish spawn than otters, and with the exception of certain wildfowl, provide no sport in return. The otter, like the fly-fisherman, is a sportsman, and for this reason the one should deal leniently with the other.
Otters do most of their feeding and travelling at night, but it is not an uncommon occurrence to find them abroad in daytime. In Canada we have on several occasions seen them on the ice during the day, and once while watching a deer runway near a river, a big otter floated downstream within twenty yards of us. Having fed up-stream during the night, an otter may take to some holt at the end of his journey, or he may float down with the current—if the water is fairly deep—and return to the holt from which he started. Although an otter can make wonderful headway against a strong current, he generally avoids rapids and rough water when travelling up-stream. On coming to such a place he lands, makes a detour, and enters the water again higher up. His « 70 » feeding expeditions are not necessarily restricted to the main river, for he often explores side-streams, ditches, and other places, which lie at a considerable distance from deep water. He usually leaves his holt—or couch if he is lying rough—about dusk, and returns to it before daybreak. For the most part otters are silent creatures, but they whistle when calling to each other, and will snort and blow when playing together. In Canada their playgrounds are the "slides," and there two otters will gambol like puppies between the intervals of tobogganing down the bank.
Although an otter does not dig to any extent, he will, as already mentioned, scratch up sand or soft earth for a certain purpose, and his feet and claws aid him in securing crustaceans and other food. Although the otter is unable to climb like the marten, he can on occasion jump and scramble over high places in a wonderful manner. In the North, otters regularly travel deep ghylls and watercourses where they are obliged to climb « 71 » to some extent, and when hard pressed by hounds it takes a very rough place indeed to stop an otter. In big coverts an otter will stand up before hounds like a fox, and will travel at a surprising pace.
On rough, rocky rivers, an otter's claws, particularly those on the hind feet, are often very much worn down. This may be accounted for by the state of the going. A mounted specimen now in our possession has the claws of the hind feet practically worn off, whereas the nails on the forefeet are nearly perfect.
There are probably few waters in Great Britain which are not at some time or other haunted by otters. Even in the vicinity of towns the marks of otters may be found beside canals and streams, the surroundings of which would appear to be anything but attractive to Lutra. Being chiefly a creature of the night, nomadic and elusive in its habits, the otter often spends a peaceful existence in the vicinity of human habitations, the occupants of which never dream that the "sly, goose-footed prowler" is a frequent visitor to their water. The « 72 » majority of people have never seen an otter, except under a glass case in some museum, or within the confines of the Zoological Gardens. The angler, fishing at dusk, may sometimes be favoured by a glimpse of an otter, bent on the same errand as himself, but as a rule few otters are seen except when put down by hounds.
CHAPTER III
OTTER-HUNTING, PAST AND PRESENT
It was not until a comparatively recent date, that the otter became an accredited beast of chase. He was hunted, after a fashion, from the very earliest times, but the value of his skin—like that of the fox—had more to do with his capture than the sport he afforded.
King John of England appears to be the first Master of Otterhounds of whom there is any record, and Twici seems to have been the first huntsman. In "The Master of Game," written between the years 1406 and 1413, there is a chapter on "The Otter and his Nature," illustrated by a reproduction of an old illumination entitled "Otter Hunting." This picture represents a « 74 » hound—apparently smooth-coated—swimming an otter in a river. On the farther bank are two hounds, and two men. One of the latter is transfixing the otter as it swims with a long-handled, three-pronged spear. The other man is apparently about to throw a similar kind of spear at the otter, while holding in his left hand a second spear with the ordinary type of single-bladed head. On the near bank are two more men, and two hounds. One of the latter appears to be rough-coated, or at any rate broken-haired, the other being a large, white, smooth-coated animal. This hound is evidently a limer, as it is held in leash by one of the men. The other man, armed with a single-bladed spear, is stabbing the otter in the hindquarters.
It is apparent that in those early days the chief use of the hounds was in finding the otter, and once the latter was put down, the spears were brought into play. In the chapter on the otter, it says: "Men hunt at them with hounds by great mastery," and "men take them at other times in « 75 » rivers with small cords as men do the fox with nets and with other gins."
Thus we see plainly that the otter was little thought of in those days, except for the value afforded by his skin. In early times a lime-hound, i.e., a hound held in leash, was used for harbouring deer and other game. Such a hound was keen and staunch, not too fast, and was taught to run mute, in order not to disturb the game whose exact whereabouts his master wished to discover. The rope by which the hound was led was known as a liam, being made of leather or silk. Both collar and lead were often gaily coloured, and adorned with silver.
The method of conducting the chase when hunting at an otter "with hounds by great mastery" was no doubt similar in some respects to that practised at present. Instead, however, of hunting the drag with the pack, lime-hounds were used to locate the quarry, the latter being then bolted by terriers. In the prologue to "The Master of Game," it says with regard to dogs: « 76 » "And first I will begin with raches (running hounds) and their nature, and then greyhounds and their nature, and then alaunts and their nature, and then spaniels and their nature, and then mastiffs that men call curs and their nature, and then of small curs that come to be terriers and their nature." What these terriers were like compared to the present-day breeds, it is difficult to say, but no doubt they were hard-bitten animals, well able to bolt otters or foxes.
Having bolted the otter, probably several hounds were then uncoupled, which kept the quarry on the move, so that the men got plenty of chances to use their spears. The otter was allowed no law as is now the custom, but was transfixed at the first opportunity. The spears were evidently thrown at the otter, as well as used to transfix him on the shallows.
At a later date, in Somervile's days (1735) the spear was in general use, and it is mentioned as late as 1878 in the "Manual of British Rural Sports" by Stonehenge. Turning to the "Otter Hunting « 77 » Diary" of the late Mr James Lomax, of Clayton Hall, which dates from 1829 to 1871, we find no mention of the spear. In "Field and Fern" (South), by H. H. Dixon, published in 1865, there is an account of Dr Grant, of Hawick, and his otterhounds, without, however, any reference to spears. Although the employment of the spear, or "otter-grains" as it was sometimes called, was no doubt almost universally discontinued fairly early in the last century, it was probably used till a later date by individuals who kept a hound or two, and pursued otter, fox, and foumart after the manner of the Scotch "tod-hunter" with his scratch pack. Nets were sometimes used in conjunction with spears to keep an otter from reaching tidal waters.
To-day, however, all such abominations have been done away with, and now it is left for hounds to hunt and kill their otter, if they can, unaided. Until a few years ago, it was customary to meet quite early in the morning, often soon after daybreak. Nowadays, however, people are less energetic, and it is nothing unusual to read of « 78 » fixtures as late as ten a.m. Although from a social or "love and lunch" point of view, late meets are no doubt convenient, the same can hardly be said as regards hunting. Some Masters of Otterhounds are averse to early meets because they say that the drag is then often so strong that hounds are very apt to pass over their otter. By getting to the water later the drag has lost some of its strength, and hounds are then brought to their noses, and travel slower, thus being less inclined to pass their otter in its holt. Really the time of meeting should depend upon the character of the water you intend to hunt. On a river flowing through marsh or water meadows, where the long grass and rushes are always more or less damp and the ground beneath them shaded from the sun, scent will lie for hours, and there is no necessity to make a very early start. In the North, however, where the streams are swift and rocky, and have their sources far up the hill-sides, there is often little shade, except beside some covert, or in some ghyll or ravine to which the sun's rays seldom penetrate. Meeting at ten o'clock on such water, there is little chance of a good drag, and it may mean hard work for both men and hounds before they find, and eventually put their otter down.
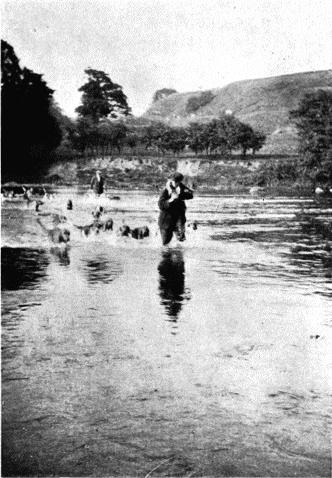

Many an instance comes to mind, when if hounds had been put to water three or four hours earlier, they would have had a hot cross-country drag, and probably a fine swimming hunt at the end of it. We have known hounds meet at nine o'clock at the foot of a Lakeland beck, and travel several miles up-stream without a whimper. On nearing the source, they spoke to a drag in the depths of a shady ghyll, and carried it at a fast pace out on to the open fell. There the sun was beating down with tremendous power, and under its influence the drag died out. Hounds were on the line of a travelling otter, and had they hit off the drag in the ghyll at five or six o'clock instead of nine, they could easily have carried it over the watershed, and down a runner which enters a tarn in the next valley. A good hunt was thus spoilt, simply because of a late start.
An advantage of meeting early lies in the fact that you perhaps find and kill your otter before the real heat of the day begins, thus making things easier for both hounds and field. It is impossible to lay down any hard and fast rule as regards the time of meeting, for as already mentioned, this will be influenced by the character of the water you are going to hunt, and, if you are dependent on subscriptions, the keenness or otherwise of your subscribers.
In the case of making a start with a newly organised pack, containing a good proportion of unentered hounds, it is advisable to get out early in the morning until such time as your hounds begin to understand their job and take an interest in the business. Scent lies stronger both on land and water during the early hours, and if your few entered hounds find and mark their otter, the unentered ones have a better chance when their quarry is eventually put down.
To a lover of hound work, the drag left by an otter during his nightly wanderings, provides as « 81 » much of interest when hounds can own it, as the actual hunting after the otter is afloat. With entered hounds which try the banks carefully it is possible to find an otter without touching a drag at all. This frequently happens after a late meet, when the huntsman is a real trier, and can depend on his hounds. Still, we imagine that the majority of keen otter-hunters enjoy watching the pack at work on a drag, and the music seems a fitting prelude to the chorus that arises when finally hounds mark and acknowledge in no uncertain tones that their quarry is "at home."
Under favourable conditions the scent of an otter will lie for a very long time. In the shade, amidst tall herbage, or among the water lilies, hounds can speak to it hours after their otter has gone, and it is sometimes difficult to know whether they are the right way or running heel. Then is the time to look for the seal of your otter in the sand, mud, or other soft places, and note whether the footprints point up-stream or down. Half the pleasure of otter-hunting is to see hounds draw, « 82 » that is if they draw well, trying every root as they go, or swimming out to some stone in midstream on which perhaps there is a piece of wedging. Here a hound will try a patch of water lilies, there another will investigate a stick-heap, until at last there is a welcome note from Thunder, Sailor, or some other member of the pack, which denotes that a drag has at last been found. Gradually they work it out, fast or slow according to its strength, until at last they mark at a tree-root on the bank. If you know your hounds you can tell pretty well whether your otter is there, or has merely run through the place and gone on. One or two of your most trusted favourites perhaps show an inclination to push forward up-stream, so you go ahead, taking plenty of time at all the likely holts. Suddenly old Warrior's head goes up, he winds the air for a second or two, then goes straight across the river, and his well-known voice rings out as he proclaims that his otter is this time in the holt in front of him. The others surge over, splashing the water as they go, and a wild chorus « 83 » awakens the echoes as hounds mark solidly, some of them tearing at the bank in their eagerness to have their quarry "out of that." There is no doubt he is at home, but if there was, you need only watch old Boatman swimming round and round beneath the holt in an endeavour to take the scent or "wash," to convince you that hounds are right.
The great advantage of meeting early lies in the fact that if there is an otter or otters working the water that you propose to hunt, you are practically sure of finding a drag, which at that time of day will lie strongly. As already mentioned, otters lie rough, as well as in holts, and may be found almost anywhere, often far from the main river. Here is where you benefit by a warm trail, for there will be no doubt as to the point at which your quarry left the main river, and took to a side-runner, or out across country to some pond or other favourite feeding ground. Supposing, however, that your otter has left a drag on the banks of the main river, which leads hounds « 84 » steadily up-stream. If the drag is hot, the pack will run it at speed, until they finally mark their otter in his holt, or the trail suddenly comes to an end, and hounds are at a loss. In this case your otter may have gone on some distance in the water, the latter having carried all scent away, and then landed at some holt farther up. He may, too, have crossed the stream—perhaps in deep water—and retired to a holt on the opposite bank. Again, he may have dropped down with the current to his original starting point, leaving no trace behind him. If the river is narrow, he may, of course, have crossed and re-crossed it in his journey up-stream, the same applying in a lesser degree, to a wide river. If possible, it is wise therefore to have a number of hounds on each bank, instead of, as some huntsmen do, crossing with the pack at shallows or other spots where the stream can be forded.
By keeping hounds on the one bank and crossing here and there, much water and many a likely holt is passed over. Harking back, however, to where « 85 » hounds checked. The otter may still be in front, therefore it pays to make good the water for some little distance up-stream. If, within a reasonable distance, hounds hit off his landing place and mark him at a holt, well and good, but if there is only a "touch" here and there on which hounds feather, denoting a stale line perhaps a day or two old, it is then advisable to try back. If hounds have carried the drag at speed, they may, in their eagerness, have overrun their otter, and left him not so very far behind. When casting back therefore, go slowly, and keep some hounds if possible on both banks. Sooner or later, with anything like luck, hounds should locate their otter on one bank or the other. Just as an early start affords a hot drag, so does it help hounds to more easily wind their otter in his holt, should he have crossed and left no trace behind him in the stream. Some hounds exhibit great aptitude for winding an otter in this manner, therefore when you see a member of the pack throw up his head and begin testing the air, you can be fairly sure that your otter is not « 86 » far off. If, instead of meeting early you had arrived at the water late, on the foregoing occasion, you would probably have hit off a weak or catchy drag, and have had to go slow, trying both banks carefully en route. If this happens on a stream which the Master knows well, and has often hunted before, he may simply cross and re-cross the water to the various holts from which he has put down otters on previous occasions. Should hounds refuse to mark at any of these holts, and the limit of the day's draw is reached, the result is a blank.
The same thing may happen on a river which has not been hunted for a long time. The meet is late, hounds are left to pick up a drag if they can, the field following at their leisure, and once more it is a case of "nothing doing" at the conclusion of the draw. It is when an otter has left the main river via a side-stream, or travelled a long way overland to some pond, or other retreat, that the advantage of meeting early is so conspicuous.
Late in the day the drag is very weak and « 87 » catchy in the open, where the sun has dried up all moisture, and even if hounds do show an inclination to turn up a runner or deviate at some point, they may not be able to carry the line far, even if encouraged to do so. If an early start is made, however, the drag is warm, and hounds can hit off the place with certainty where their otter has left the river, and what is more, they can run the line at speed, thus drawing up to their quarry's holt, or the spot where he is lying rough, without loss of time. The chief object of keeping a pack of otterhounds is to find, hunt, and if possible kill your otter in a sportsmanlike manner.
Before you can hunt him you must find him, and on nine days out of ten, this is the hardest part of the business. An otter may be anywhere, and of course it may so happen that the water within your day's draw is not being worked by otters. In this case you cannot find what is not there. A blank day then is not only excusable, but inevitable. On the other hand, if your pack is made up of entered hounds, and you know their individual idiosyncrasies, « 88 » and have in addition a fair knowledge of the habits of your quarry, there should be little excuse for a blank day, provided you start early enough in the morning to afford your hounds the chance of picking up and sticking to a decent drag. The surest way of finding an otter is to drag up to him, any other method, at any rate on rivers, holds an enormous element of chance. On a lake or a tarn, which you yourself know is inhabited by otters, it is a different matter, for you can then throw off in the reed-beds or other undergrowth bordering the water, with a good hope of putting your otter down before hounds have been long at work.
No fixed rules are applicable to otter-hunting, or any other kind of hunting for that matter, but it is safe to say that the Master who is a trier, and keeps on trying, will be the one to bring to hand most otters. Being himself of the "never say die" order, he will inculcate the same spirit in his hounds, for a slack huntsman makes a slack pack, and vice versa.
The late Rev. Jack Russell, of Devonshire fame, walked some hundreds of miles before he found his first otter. This was owing to the fact that his hounds at the beginning were unentered to otter. When he finally got hold of an entered hound, matters took a different turn, and he showed capital sport, but his ill-success at first was certainly not for want of trying.
When hunting a river, particularly in a hilly district, a sudden flood may put a stop to sport. When the weather is unsettled it is wise, therefore, to allow for such a contingency, and be prepared to arrange matters so that a smaller stream or lake can be substituted.
A frequent reason for blank days lies in having too wide a district to hunt. This means that certain streams are visited but once a season, and a single day on each is not sufficient to insure sport. A certain river is perhaps visited to-day, and hounds hit off a drag and carry it up-stream a long way, until the hour is late, and their otter still unfound. The next fixture is probably in another « 90 » county, whereas if hounds were put to water on the following morning at the place where they left off, a hunt would be practically a certainty. Again, if a brace of otters are put down, and one of them is hunted and eventually killed, a visit to the same water on the following day would result in the survivor providing some pretty work for hounds. There is hardly an Otter Hunt in the kingdom but what attempts to cover more water in a season than it can properly manage. The chances of continuous good sport are on this account exceedingly doubtful, for unless rivers are frequently visited, and a fair percentage of otters are killed, riparian owners, keepers, and others will refuse to protect otters, and instead, go in for the killing business themselves. Hunting is in this country dependent upon the goodwill of landowners and tenants, who are as a rule only too pleased to welcome hounds. If, however, the Hunt does not properly reduce the stock of foxes or otters, other methods are then resorted to. The more otters or foxes you kill in your district, the « 91 » more you will have, for directly people realise that you and your hounds mean business and are "out for blood," they will leave it to you to do the killing, and confine their attentions to preserving your quarry. A small district, regularly hunted, will provide much better sport than a large one casually attended to. The fixture card of the average Otter Hunt should show "Where leave off" much oftener than it does at present. In a small district a Hunt is much less dependent on trains for moving hounds from place to place, and there is far more opportunity to "lie out" overnight at some farm or other homestead, and thus continue hunting at the same place on the following day.
Harking back to the river, a great many people imagine that when hounds hit off a line away from the water, and go full cry through a wood, across open country, or up some tiny streamlet, that they are running riot. That hounds occasionally run riot, more especially the young entry, we do not for a moment deny, but when a pack of entered hounds performs in the above manner, they are « 92 » not rioting, but running the line of a travelling otter. The huntsman then, instead of blowing his horn while the whippers-in rate and attempt to stop hounds, should put his best leg foremost and try to keep in touch, so that if hounds check, after covering perhaps a mile or two, he will be there or thereabouts and have a good idea what to do.
We have vivid recollections of a day on which hounds hit off the line of an otter that had stolen away from a rock-holt without being seen or tallied. She, for it was a young bitch otter, left the main stream with a good start, and turned up a runner which lay in a deep, narrow valley. At the head of this valley the otter turned left-handed and crossed over more than a mile of open country comprising the watershed. Descending the other side, she entered a stream via a hanging covert on the near bank. When hounds hit off her line, they raced up the valley with evidently a screaming scent. At the top they hovered for an instant, then swept on left-handed over the hill. The huntsman, who was convinced that they were running « 93 » riot, attempted to stop them, and succeeded in getting hold of some of them, but the others went on, and we could hear them speaking merrily in the direction of the stream in the valley below. We passed the huntsman, blowing his horn, with a couple or two of hounds round him, and on asking him what was the matter, he said hounds were rioting. Seeing we did not believe him, he reluctantly followed on, and to cut a long story short, hounds eventually killed their otter handsomely, after dusting her up and down the stream for some three-quarters of an hour. We can see the expression on that huntsman's face yet, when hounds collared their otter, and he was obliged to acknowledge he had been in the wrong, while his hounds had been right.
Now the first lesson a huntsman, professional or amateur, has to learn is to trust his hounds. If he can't do this, he had better leave hunting alone, and look for another job. Once your hounds are properly entered, and you know their individual traits and idiosyncrasies, always trust « 94 » to what they say about it, and pay no attention to the utterances of a sceptical field, many of whom know little or nothing about the science of hunting. The line hounds are running may perhaps seem a very unusual one, even to you, but if Rouser, Thunder, Marksman, and a few more of your trusted favourites are voicing the fact that an otter is in front of them, then you can bet your life it is so, and your job is to keep in touch with them if possible. Always remember that an otter may be found anywhere, and may do anything once he is afoot or afloat. The only certain thing about him is his variability. You will learn something new about him every day you go out with hounds, and if you store up the information thus obtained, it will come in mighty useful on many a future occasion.
The Master who hunts his own hounds should study the habits of otters in winter as well as in summer. After a prolonged snow-fall a visit to one or other of his rivers, lakes, etc., will afford a variety of useful information regarding the whereabouts « 95 » and the doings of otters. Their tracks will be plain enough in the snow, and by following these footprints a knowledge of the various routes traversed by otters will be gained, and many a long forgotten drain or other hiding-place discovered. The lessons thus learnt will come in mighty useful when the hunting season again begins. When thus scouting his country, he should not forget to drop in at the mill, or the various farmsteads near the river. The miller can be a good friend, or, if he likes, a bad enemy, and the same applies to farm-hands, and other people who work on the land. A chat with the farmer and his wife goes a long way towards smoothing the ground for hunting, and a friendly word and a pipe of baccy with the river-watchers and labourers ensures amicable relations, and paves the way towards encouraging an interest in hounds and hunting.
It is the Master who is thus on the job in winter as well as summer who gets plenty of good walks for his puppies, and is free to hunt when and where he likes during the season. On his journeys he « 96 » will hear much about otters and their doings, a great deal of which information, however, he will take with the proverbial pinch of salt. Half the people you meet, even those who live near rivers, have never seen an otter, although there are, of course, certain individuals whose information is to be depended on. These are few and far between, however, and the wise Master will trust to his own powers of observation, rather than to reports of hypothetical otters, which in the end turn out to have been black cats, or some other animals seen near the water at dusk.
Harking back to our hunting, however, hounds have marked their otter in his holt in a root or some other retreat, and the next job is to evict him. Hounds are called off and taken back out of sight in a nearby field, and the terriers come on the scene. Vic or Vengeance is sent in, and very soon there are sounds underground betokening "something doing." The barking ceases for a moment, and then a dark brown object glides out through the tangled roots, there is a slight splash, « 97 » and a long chain of bubbles as the otter takes to the river. A shrill tally-ho! brings hounds pell-mell to the scene of action, and the hunt is on. It all sounds very easy, and sometimes is so, but on other occasions the otter refuses to bolt, or the terriers cannot bring sufficient pressure to bear, so there is nothing for it but send to the nearest farmhouse for tools. Spades, pick, and crowbar are soon on the spot, and there may then ensue some strenuous digging, before the terriers are located, and finally the otter. Occasionally, when the terriers are sent in, a rabbit or rabbits may bolt, or even as has happened before now, a fox. Then is the time you are likely to hear subdued remarks from sceptical members of your field. Take no notice of that. Your hounds say their otter is there, believe them, no matter how many rabbits appear. Otters lie very close at times, often till you dig right up to them, and on such an occasion you will have the laugh on the "doubting Thomases," when you pull little terrier Vengeance out by the stern, and your otter takes to the river. « 98 » If a terrier can get behind his otter, he will generally persuade the quarry to bolt, but if the otter backs up into a cul-de-sac, the dog is obliged to face him in front, and if the terrier is a real "sticker" he will hold his otter there until the diggers work down to the spot.
Otters will lie up in rabbit burrows, drains, tree-roots, and sometimes in fox or badger earths. Rock-holts are also favourite places on the north country rivers. Where there are several side-drains branching off a main drain, it is often difficult for the terriers to locate their otter. Some rock-holts, too, are practically impregnable, and the same applies to many a big head of earths in covert. Occasionally an otter may be persuaded to bolt when other means have failed, by getting a number of people to jump on top of the holt, the party doing so in unison. When digging or terrier operations are going on, someone should be stationed where they can keep watch for the otter bolting. If the quarry can slip out under water, he may get away undetected, unless a bright look out is kept. « 99 » During the time that digging is going on, the field should be made to stand well back from the scene of operations. When they crowd round the place, as the average field so often does, they are a nuisance to the diggers, and talk so much that it is often impossible to hear the terriers underground. Again, should an otter bolt from a drain, and have some distance to go before reaching the water, the field are nearly sure to start halloing, with the result that hounds break away and arrive on the scene ere the otter has had fair law.
Once the otter is afloat, the next thing is to keep him going until hounds tire him out, and at last gain their reward. The field should now spread out at intervals, along the bank, and stand still. By doing so each individual can watch the water in front of him, and tally when he is certain he sees the otter. When the field persists in rushing up and down the banks they are a nuisance to both hounds and huntsman. Standing still, and keeping a bright look out, they can be of the greatest service, and at the same time they see « 100 » more sport than when constantly shifting their positions. After he has been hunted for some time, the otter will begin to show himself, and it is then perfectly legitimate for the watcher to tally-ho if he sees the otter. Unless, however, he is sure that it is the otter, he had best keep silent. A salmon in rapid water, or a moorhen crossing a pool, has often deceived a watcher on the bank, therefore make sure before tallying. Also, never tally because someone else says he has seen the otter, see it yourself first. It may be necessary to send some of the field to form a "stickle" across the shallows, above or below the scene of action. These people must keep a sharp look out, watching the water carefully. If they do their work properly, the otter should not get past them without being seen. If the hunt gradually works up-stream, the people on the lower stickle should not be forgotten. Some signal, say a few notes on the whistle, should be given in order to let them know that they are at liberty to leave their posts.
 TALLY-HO!
TALLY-HO!In rapid, or deep water, an otter will often pass an experienced hunter without being tallied, particularly if it is moving close to the farther bank. The angle at which the light falls on the water often makes it extremely difficult to detect an otter as it passes. After being hunted for some length of time, the otter shows himself more and more frequently. He may vary the water work by making an excursion overland, or running the length of a nearby wood. Perhaps he takes refuge in a holt, and is then bolted by the terriers. Anyway, if things go right, the time comes when he can do no more, and he dies fighting on the shallows, leaving his mark on nearly every hound. The huntsman at last gets the pack to leave him, not using a whip, but pushing hounds off with knees, hands, and pole, after which he slips the carcass under water for a minute or two until he recovers his wind, and then carries it ashore. There it is weighed, mask, pole, and pads are severed, the carcass is slit up, and tossed to the eagerly expectant pack. "Hi, worry, worry, worry," "Who-whoop! tear him and eat him." After blowing the "rattle," and cheering hounds to keep up the excitement, the various trophies are distributed, and one's thoughts then turn in the direction of certain bottles which are snugly reposing in a friend's car on the nearest highway.


Early, or late in the season, when the weather is boisterous and the water cold, it pays to hold up a few couples of hounds, reserving them until the working pack has had about enough of it. Then at the right moment, throw in your reserves and make a quick finish. This plan is especially applicable to lake hunting, when hounds are continually swimming in deep water.
When hounds are on a drag, or have put down their otter, the huntsman should encourage them, cheering them on to any particular hound which has made a hit, and the same when they mark solidly at a root. There is no need to be noisy, but hounds work all the better for encouragement, and a bit of excitement at a holt teaches young hounds to mark their otter. To make a success of otter-hunting, or any other kind of hunting for « 104 » that matter, a man must use his brains, and to some extent call on his powers of imagination.
A chapter on hunting is hardly complete without some mention of that elusive mystery called scent, so a few words will be devoted to it here. You get good and bad scenting days in otter-hunting just as you do when hunting fox or hare, but the chase of the otter has the advantage of being conducted both on land and water, and if scent is bad on the latter, it may be quite the reverse if your otter takes to terra firma. Sometimes it is good on both, though it may happen that an otter which has been hustled about the woods or across country apparently gives off little scent when he returns to the water. A bitch otter in cub, or one with a young family, appears to often give off little or no scent, and where hunting takes place on a river polluted by oil, or other foreign matter, scent is generally conspicuous by its absence. Scent varies too at different times of day. In the early morning, before the sun has dispelled the dew, it is generally good, but dies « 105 » away as the atmosphere becomes warmer. When the sun begins to sink and the air becomes damp again, scent is likely to freshen; while a shower of rain may affect it in the same way. The vagaries of scent are impossible to foretell with anything like certainty, and perhaps it is as well so, otherwise sport would become too cut and dried, and would lose much of its interest on that account.
Occasionally an otter takes refuge behind weiring or in some other retreat, that necessitates pulling down a certain amount of the obstruction before he can be evicted. In this case, permission from the owner or tenant of the place should be obtained before beginning operations. In the same way, should the owner or tenant object to the presence of hounds on his land, always be civil, no matter what he says, and take hounds away without any argument. The life of the sport depends upon the existence of amicable relations between the Hunt and the owners of the land which they cross. Although terriers can as a rule bolt an otter if they can get to him, ferrets have been used « 106 » for the same purpose before to-day. Both otters and foxes have on occasion been bolted from rabbit burrows during ferreting operations. In some countries artificial drains or holts have been constructed for the use of otters, but there is usually a good deal of uncertainty as to whether the otters will take to such abodes. Where old drains run a long way into the land, with possibly a number of branch drains, it is often wise to place iron gratings at some distance from the mouth, in order to facilitate matters when it comes to bolting an otter. As the great charm about otter-hunting is its freedom from artificiality, made holts or drains need hardly be encouraged, except perhaps in extreme cases where there is no suitable lying-up place for otters over a long stretch of water.
When hunting hounds, the Master will be assisted in the field by two whippers-in, which may consist of the paid kennelman, and an amateur. Their job is to keep hounds in check when necessary, prevent rioting, if any, and keep in touch with the pack should hounds go off across « 107 » country with a screaming scent. Taking it for granted that the paid hand knows his job, the amateur should be equally proficient. He must keep a keen look out as he goes for signs of otters, as well as hidden drains, etc., and he must know the names of all the hounds and their individual idiosyncrasies, so as to tell instantly if they are inclined to riot, or they show an inclination to mark at roots, or take a line away from the river. Speaking broadly, the whippers-in prevent hounds going too fast and outpacing the Master and the field, but it should be remembered that hounds can be kept too much in check, and by so doing they are balked in their desire to hunt, as well as drive on when scenting conditions are good. In fox or hare hunting, the huntsman's place is with his hounds, whether they are drawing or running, and there appears to be no good reason why an otter-huntsman should not "get a move on" when his hounds push ahead on a hot drag, or drive along across country. It is quite as necessary to run, and often run hard, with otterhounds, as to ride hard « 108 » with foxhounds, and the huntsman who takes his own time whilst his whipper-in is bursting himself across country is surely lacking in keenness.
Although otter-hunting does not call for as much quickness on the part of the huntsman as fox-hunting, we still must confess we like to see a huntsman of otterhounds show some agility when his hounds run fast. This particularly applies to hunting in the north, where otters so often cross steep watersheds. A great deal of valuable time is frequently lost, simply because the huntsman prefers to take his own time, instead of attempting to keep in close touch with hounds, and thus be on the spot should they momentarily require his assistance. As far as the field are concerned, it is their own fault if they are left behind when hounds run. When travelling with hounds on the highway, however, the huntsman and whippers-in should go at a reasonable pace, so as to give the field a chance—particularly the ladies—to be there when hounds are put to water. Racing ahead with hounds on the roads gets the pack into the habit of pushing « 109 » on when there is really no need for it, so a reasonable walking pace should be aimed at.
When hounds have put their otter down, or "hit him abroad," to use an old expression, and are swimming him, the huntsman should keep on the shallow side of the river, more particularly if the farther bank is thickly overgrown with willows or other cover. From the shallow side he has a clear view of what his hounds are doing, and if it is necessary to pole the farther bank if an otter persists in hanging there, he should ask one of his whippers-in, or some experienced member of the field to do it for him.
With regard to clothing and etceteras for otter-hunting, little need be said here. Hunt uniforms are usually made of woollen serge material, which dries quickly, and withstands a lot of rough usage. Shorts are sometimes worn, but in our experience loose knickerbockers are much preferable, particularly for hunt officials who may have to force their way through briers or other undergrowth in the execution of their duty. Bare « 110 » knees and thorns do not associate well together, while breeches of the semi-riding type are too tight-fitting, and retain water. Boots or shoes should be well nailed to prevent slipping, preferably with soft, wrought-iron hobs, which get a better grip on rocks than steel nails. An iron-shod pole of ash or hazel—the latter is light yet strong—is necessary for crossing deep or swift water, and in some districts as an aid to jumping wide ditches and open drains. A pole shod with a double-pronged spike is less liable to slip than one armed with a single spike. Likewise a pole cut from the growing tree or sapling looks more workmanlike than a "made" one, ornamented with a fancy metal head or other embellishment. With regard to the whip, for use by Hunt officials, one with a short lash is to be preferred, for it can be far more easily cracked when the user is standing in water than a long-lashed affair.
The huntsman who cannot blow an ordinary horn without unnecessary discords will be well advised to secure a reed-horn. Every call can be « 111 » sounded on this, with the exception of that "to call hounds away," and for this quite a good substitute can be blown. When using the horn, he should employ distinct calls, then both hounds and field know what he means. Some huntsmen blow the same note all day long, and hounds take no heed of it, while the monotonous sound gets on the nerves of the field.
Nowadays the otter-hunting season extends from April to September, but in the fourteenth century it lasted from February to June.
CHAPTER IV
HOUNDS AND TERRIERS
The average otterhound pack to-day is usually composed of foxhounds, cross-bred hounds, and a few couples of pure, rough-coated otterhounds. In the old days the latter predominated in most packs, and it is only of late years that the foxhound has come to the fore in the pursuit of Lutra.
The origin of the rough-coated hound is more or less shrouded in mystery, but it is pretty safe to say that he is closely related to the bloodhound. If true to type he possesses many of the bloodhound's characteristics, including the long pendulous ears, the deep-set eye showing the haw, and the black and tan colour which so often predominates. The rough coat was gained by a cross of some sort, but it is impossible to say with certainty « 113 » what this cross was. The wire-haired Welsh harrier may have had something to do with it, and again it is quite likely that the old hard-coated Lancashire harrier may have been used for the same purpose. It is possible, too, that the old southern hound was crossed with the bloodhound, while there are those who believe that the French griffon had a share in the business. Thus we see that the rough outer coat may have come from a variety of sources, but the thick, woolly under-coat is no doubt a provision of nature to protect the hound from the effects of frequent and long-continued immersion in the water. This under coat is worn by the Chesapeake Bay dog, a breed of retriever much used by wildfowl shooters in America.
In the fourteenth century raches or running hounds—known later simply as hounds—were of various kinds. In the "Master of Game" it says: "There be also many kinds of running hounds, some small and some big, and the small be called kenets, and these hounds run well to all manner « 114 » of game, and they (that) serve for all game men call them harriers. And every hound that hath that courage will come to be a harrier by nature with little making."
Harrier was in those days spelt heyrer, and it was not until after the sixteenth century that the modern spelling came into vogue. It was probably derived from the Anglo-Saxon herian, to harry or disturb. In the "Boke of St Albans" it says that the hart, the buck, and the boar should be started by a limer, and that all "other bestes that huntyd shall be sought for and found by Ratches so free." Thus it appears that all beasts that were enchased were moved by a lime-hound, while those that were hunted up were found by raches. The otter-hunting illustration in the "Master of Game" shows five hounds, one of which is on leash, and appears to be a limer. The otter was certainly not enchased in those days, being looked upon as vermin, yet as the picture shows a limer at work, it is possible that lime-hounds were sometimes used for other game than « 115 » the recognised beasts of chase. The hound shown swimming the otter is bloodhound-like, while two smaller hounds appear to have broken coats. In the fourteenth century the otter and various other creatures, such as the rabbit, fox, wild cat, etc., were hunted by biss hunters (fur hunters) for their skins, and no doubt the smaller breed of hounds then known as heyrers were employed in their capture.
Coming down to modern times, there are, as far as we are aware, but two existing otterhound packs entirely composed of pure, rough-coated otterhounds. All other establishments employ mixed packs. Cross-bred hounds are usually the result of a union between a pure otterhound bitch and a foxhound. The majority of foxhounds which find their way to the otterhound kennels have been drafted for over-height, age, or faults. They are often presented to the M.O.H., or he buys them at a low figure. Having purchased or otherwise got together sufficient hounds to make a start, you can gradually weed them out, retaining the best « 116 » workers for future breeding operations. It is perhaps unnecessary to state that you must have a couple or two of entered hounds to begin with, otherwise you are likely to walk as far as the Rev. Jack Russell did before you find an otter. As regards cross-bred hounds, the first cross may be capital workers, but it is doubtful if much good comes from breeding from them.
One sees all shapes, makes, and sizes of rough hounds in the various packs, but the best bred ones are big, upstanding animals, from twenty-two to twenty-four or more inches in height. Speaking from our own experience, we have found the majority of rough hounds to be much more clumsy and less active than foxhounds. Their feet, too, are often inclined to be open and flat, and they lack the heart and stamina of the foxhound. There are, of course, exceptions, and we have come across rough hounds that were capital workers, but take them all round they are too big and clumsy, at any rate for work on rough, rocky streams. Despite their rough jackets, they suffer from the effects of long immersion in water far more than the foxhound, whose short, smooth coat is dry after a shake or two. In addition they are not such good doers as the foxhound, and require more attention after hunting. They are also apt to be quarrelsome in kennel. Many of them possess extremely fine noses, and can speak to a line a day or two old, but this is of no practical help in hunting, because it is impossible to drag up to an otter that has been so long gone. They swim well, and often draw well when swimming, but the foxhound is quite their equal in this respect. In our experience the hound that can wind his otter across the stream and go straight to him is more often a foxhound than a rough hound.


The foxhound, too, is usually a better marker once he has entered properly, and when it comes to holding and killing an otter, the rough hound cannot compare with him. Across country, too, and when an otter runs through covert, the foxhound's dash and drive at once put him in the « 118 » lead. The rough hound has a resonant, musical voice, and a picturesque appearance, but taking him all round, from a solely working point of view, he is, in our humble opinion, inferior to the foxhound, particularly on rough, rocky rivers, where a light-built, active type of hound shows to advantage. Custom ordains that hounds for otter-hunting should be rough jacketed, and by employing cross-bred or rough Welsh foxhounds you get the rough coat, without the undesirable qualities found in the pure otterhounds.
The latter show to the best advantage in low-lying country, where the rivers are slow running, and the going easy. In these days, when meets are late and time is valuable, pure otterhounds with their tender noses dwell and revel on the drag instead of pushing forward. The foxhound, on the other hand, may feather on a stale line, but he will not as a rule open unless the drag is fairly fresh. When he does throw his tongue, you can confidently cheer the others to him, knowing that your otter is not so very far in front. Although « 119 » we cannot deny that the deep, resonant music of a pack of pure otterhounds is delightful to listen to, something more than the "band" is required to kill an otter.
Foxhounds, cross-breds, and Welsh hounds throw their tongues well enough, and in addition they possess dash and drive, with little or no inclination to dwell. Foxhounds, before they have entered properly, draw wide and will not always stick to the river, but if they have done a few season's stag-hunting—thus being used to water work—they generally enter well to otter and draw closely enough. A hound may not take any interest in the sport during his first season, but the following season he may prove to be one of the best. Unfortunately the majority of draft foxhounds are aged before they find their way to the otterhound kennels, therefore any lengthy delay in entering to their new quarry shortens the period of their usefulness, that at the best cannot be very long.
Aged foxhounds after a time show an inclination « 120 » to dwell and revel in the scent, and when this happens it is a sign that their utility is coming to an end. If possible always get hold of foxhounds which throw their tongues freely, and have nothing whatever to do with a mute hound. However closely you keep an eye on the latter, he will sooner or later get away "on his own," and be the means of spoiling more than one good hunt. No matter how good a mute hound is in his work, get rid of him, for unless he lets you know what he is doing he is useless to you. Likewise, never on any consideration be tempted to breed from a mute hound. Rough otterhounds cannot stand punishment like the foxhound, and will howl and kick up a dreadful racket if hurt, or hit with the whip for some fault.
It is during the course of a long hunt in heavy or chilly water that the average rough otterhound will pull out and sit shivering on the bank, while the foxhounds are keeping their otter on the move. In our experience, the foxhound is a much better fresh-finder than the pure otterhound, and it is « 121 » the hounds good at fresh-finding and keeping their otter going that do most towards bringing the quarry to hand. At the end of a long day, too, the cross-breds and foxhounds will return to kennels with their sterns up, while many of the rough sort exhibit a very depressed appearance. They never seem to pick their feet up like a foxhound, but shuffle about in an ungainly fashion. When it comes to killing an otter, the foxhound has it all his own way. Time and again we have seen him seize and hold a big otter, often shaking his quarry like a fox. The rough hound often fails in this respect, for he has not the courage to make him a good seizer and killer. A foxhound which comes to the otterhound kennels with the reputation of being a good marker nearly always keeps up his fame in the same way when entered to otter. Good marking hounds are the mainstay of any pack. As far as brains are concerned, the foxhound appears to make more use of his "grey matter" than the rough hound, and shows more initiative and « 122 » individuality. His pace and activity, too, are beyond question, both of which qualities are of the greatest assistance when swimming an otter, and more particularly when hunting one across country or through extensive coverts. It is the active hounds which score so often on rough and rocky rivers, for drive and pace are an occasion quite as necessary in otter-hunting as fox-hunting.
The cross between foxhound and rough otterhound possesses many of the attributes of the former, including a rough jacket, and thus is admirably fitted for the pursuit of Lutra.
Turning to Welsh hounds, some of which have rough, and others smooth coats, we find a breed admirably suited to both fox and otter-hunting. Many Welsh hounds are white or nearly so, while others are the old black-and-tan colour. The English foxhound of standard type is bigger and has more substance than the Welsh hound, but the latter excels in nose and tongue, and can stand any amount of hard work in rough country. In our experience, too, Welsh hounds—particularly « 123 » those of the smaller type—are very active, and have plenty of drive, while they are often capital markers, and can hold and kill an otter quite as quickly as any English foxhound.
Another type of hound admirably suited to otter-hunting is the fell-foxhound of Cumberland and Westmorland. He is for the most part a light-built, active sort, with a capital nose, and any amount of tongue. In the Lakes and certain districts adjoining, fell-hounds often hunt fox in winter and otter in summer. The fell-hounds are kennelled in the fox-hunting season, but go out to walk in summer, and generally a few couples are lent to the local otterhounds for the chase of Lutra. In our experience fell-hounds enter quickly to otter, and on our rough and rocky northern rivers they are very hard to beat as all round performers. Many of them are capital markers, and they will hunt a drag, and kill an otter with the best.
Turning to the "Otter-hunting Diary" of the late Mr James Lomax, of Clayton Hall, who « 124 » kept a pack from 1829 to 1871, we find an illustration of the old Lancashire harrier or foumart-hound. The picture shows a couple of rough-haired hounds in full cry, which appear a medium-sized, light-built, active type; more suggestive of the rough Welsh foxhound than the modern otterhound. Mr Lomax used these foumart-hounds in crossing with his otterhounds. In another illustration, showing some of the pack in 1835, the type of hound appears to be lighter-built and more active-looking than the big, present-day rough otterhound.
The tendency with English foxhounds has been to breed them much bigger than was the case in former years, and the same apparently applies to the rough otterhound. Certainly a tall hound can wade where a smaller hound is obliged to swim, but a medium-sized, active type is less clumsy, and more fitted for work on rocky streams than the heavy hounds now seen in most packs. From a purely working point of view, a pack composed of English, Welsh, and fell-foxhounds « 125 » would be very hard to beat. By judicious crossing, an ideal pack could be bred, retaining to a great extent the rough coat of the Welsh hound, if that was thought indispensable to the appearance of the pack.
Although draft foxhounds are generally used for otter-hunting, it pays to get hold of a bitch or two and breed from them. By so doing you can gradually get together a pack composed of hounds of the desired sort, and if you are lucky you may be able to hunt fox with them in the winter, and thus keep hounds in condition for their summer work. Hounds, like human beings, get very fed-up with continual road exercise, therefore a bit of winter hunting appeals to them far more than the dull routine of exercise walks.
Next in importance to the hounds are the terriers, for without their help it would be impossible to eject an otter from his holt. The most important quality in a terrier is gameness, for no matter how well built he is, if he has not the courage to go below ground and stay with « 126 » his otter until the latter bolts, or the diggers unearth him, he is not worth his keep. Provided he is thoroughly game, and not too big, it matters not how a terrier is bred. He is there to work, and not to be looked at. Roughly speaking, a terrier of about 14 lb. weight will be suited to otter-hunting. As, apart from bolting otters, he will not be called upon to do any great amount of travelling over rough country, short legs are no great drawback to him. For all that, however, we like to see a terrier with a fair length of leg, for there are certain holts, particularly amongst rocks, where an otter can command the upper position, and a short-legged terrier is much handicapped when trying to get at him. A terrier should have a fair head and jaw, and he should be as narrow in front as is compatible with adequate heart and lung room. A narrow-fronted dog can always get into a smaller place than a broad-chested one, even if he is longer on the leg. A terrier that will lie up close to an otter and move him with his tongue is preferable « 127 » to one that goes straight in to the attack. His barking eventually gets on the otter's nerves and causes him to get "out of that," while should the otter refuse to bolt, the terrier's voice is a guide as to where to dig. A terrier soon learns his job, and after getting mauled a time or two by otters, he will make more use of his tongue than his teeth. When entering a puppy for the first time, choose an easy place, so that the youngster has a fair chance to get in touch with his otter.
As to the colour of a terrier, good ones—like horses—come in all colours. White is perhaps preferable, as a white terrier is less likely to be mistaken for the otter by hounds at a kill. Certainly white terriers appear to suffer fewer casualties in this respect than coloured ones. As to whether terriers should run loose with hounds is a question the Master must settle for himself. When terriers are loose, there is always the chance that cubs may be chopped by them, though to set against such a contretemps, many « 128 » an otter is found and put down by the terriers. Again, coloured terriers running loose may be killed or badly mauled by hounds, when the latter are hard at their otter.
During the season of 1921, with the K. and D.O.H., we had two coloured terriers worried by hounds, one of which recovered but the other died the same night. The otter, which was getting beat, took to land, and hounds collared him as he left the water, the terriers being seized by some of the pack in mistake for their quarry. Had those terriers been in the couples at the time, they would have been saved. It is really safest to lead the terriers until they are wanted, and after bolting their otter they should be got hold of again as soon as possible. The same when hounds are worrying their otter, always pick up the terriers if any of them are loose.
In order that hounds shall keep fit and well, they must receive proper attention in the kennel. Less flesh is needed for feeding otterhounds than foxhounds, because they do their work in « 129 » summer, and both the season of the year and the work itself do not make so great a call on their powers as does the chase of the fox in winter. During the off season, otterhounds should be exercised for two or three hours daily, and as the hunting season approaches the exercise can be gradually lengthened. With a pack of cross-bred, Welsh, or English foxhounds, it is possible to hunt otters in summer and fox in winter, and where this can be done, hounds will, of course, keep perfectly fit. In the case of the fell-foxhounds, those hunting otter in summer return to their own kennels for the winter fox-catching. As far as food is concerned, this should always be given thick, rather than soft and sloppy. Hounds splash "slop" into their eyes, and get particles of it up their nostrils, to the detriment of both sight and olfactory powers. On the return from hunting, cuts and bruises should be attended to, and thorns, etc., extracted. Hounds' coats should also be brushed, and burrs, etc., removed. Rough hounds require more looking « 130 » after in this respect than smooth-coated ones. The huntsman should see that his hounds are fed and properly bedded down before he attends to his own wants. If hounds look well and hunt well, you can rest assured that your huntsman or feeder is paying proper attention to the pack in kennel. As regards kennels, these need not be of an expensive nature, but the drainage and general sanitation must be adequate if hounds are to keep fit. Wherever waste matter is present, either in the boiling house, feeding place, or yards, there will disease germs gather, and complaints amongst hounds will be for ever breaking out. The old adage "Cleanliness is next to godliness" applies as much to hounds and their kennels as it does to human beings and their houses.
Some huntsmen are apt to let hounds get very much out of condition during the winter months, instead of exercising regularly, which means that on the approach of the hunting season all sorts of physic is used in an attempt to get them fit « 131 » again. It is quite safe to say that the less medicine you employ about the kennels the better, and there will be little or no need for it if hounds are rationally fed and exercised in the winter.
CHAPTER V
REMINISCENCES
There are very few Masters in the country who hunt fox in winter and otter in summer with the same hounds, and fewer still we imagine who have killed an otter and a fox on the same day. The latter feat was performed by the Master of the South Tetcott, whose hounds found and killed an otter on the River Othery, after which they unkennelled a fox cub, and after rattling him about a bit, eventually brought him to hand.
One of the few packs hunting both fox and otter is the Ynsfor, a private pack owned by Major Evan Jones. His country lies in Carnarvon and Merioneth, Snowdon and the adjoining mountains lying within its borders. The Master is his own huntsman, and hounds are followed on foot, owing « 133 » to the precipitous nature of the country. The pack is composed of the old Welsh breed, some rough and some smooth, with many of the old black-and-tan colour amongst them. These hounds have been in Major Jones's family since 1765.
Probably few people have been out with both foxhounds and otterhounds on the same day, but we can plead guilty to having accomplished this feat. Before the L.D.O.H. were disbanded, hounds met very early one morning, but failed to get an otter afloat, and when they returned to kennels we went off and joined the Coniston Foxhounds, and eventually saw Reynard accounted for.
A great many people appear to have a rooted idea that an otter is a slow-moving, clumsy creature, which never leaves the vicinity of water. Such an assumption is, to say the least of it, inaccurate, as anyone can easily testify, particularly those who have done much otter-hunting on the rocky rivers of the north. In a previous chapter we have « 134 » mentioned a hunt during which the otter crossed a watershed, and this brings to mind a seven and a half hours' hunt by the K. and D.O.H. on the River Lune in the season of 1921. The otter was lying rough in a hanging wood overlooking the river, and was found by a little fell-foxhound named Cragsman, belonging to the Ullswater pack. After some up and down work on the river, our otter stole away on land, and crossed some fields to a small stream which runs between steep banks. There was a screaming scent, and hounds fairly flew in pursuit. The otter ran the small stream nearly to the top of the ghyll, then turned and came back. In a rock-bound pool he lay low, but hounds were soon at him again. The pool lay between smooth and slippery walls of rock, and at first the otter barely showed his nose. Suddenly, however, he made a terrific spring—his hind legs no doubt getting purchase on a ledge below the surface of the water—and all but got clear of the pool. He hung for a brief instant on the rock wall, making the picture of a lifetime for anyone « 135 » lucky enough to have been there with a camera, then he turned and fell with a splash into the pool. It was a miracle how he got clear, but get away he did to run the fields again, and take refuge in a rabbit burrow on the bank of the main river. Hounds were taken away, and after a bit of work the terriers bolted him. He took down stream, and after the pack was laid on, a couple of hounds collared him on the shallows. He appeared to fling these hounds off as if they were straws, then he shot into a pool, raising a splash and a wake like a hydroplane as he crossed it.
Reaching the farther bank, he at once took to the hanging wood, and went straight up it. He gained a short start by this manœuvre, then the pack was roaring in his wake. Running the wood like a fox, it looked at first as if he was going right out at the top, but he turned and came down again, crossed the river and took refuge in a strong root holt. Some time was spent digging before he could be ejected, and when he was at last obliged to bolt, he again went straight across the river and « 136 » took to the wood. Hounds drove him round it, and he once more took the water. Here he entered a long but not very deep pool, and hounds swam him down it, then he turned and hounds checked. There was little or no cover on the banks, but he got out without being seen, the first warning we had of his departure being given by a young, rough hound which hit off his line in the wood. This time he ran straight out to the top of the covert, turned left-handed and crossed the open fields for more than a mile, just beating hounds to a drain, the grating of which had been moved, where he got in and was eventually left.
We viewed this otter several times at close quarters, and estimated his weight at nearer 30 lb. than 25 lb.
He showed extraordinary running powers and activity for so large an otter, and it was hard luck on hounds that he beat them.
There was a screaming scent on land, but when he took the water for the last time, hounds had « 137 » some difficulty in owning the wash. That otter would most certainly have convinced anyone who was sceptical of Lutra's activity and running powers.
We have already mentioned the fondness that otters have—particularly in Canada—for sliding. When engaged in this amusement, they tuck their forelegs in, and toboggan down the bank on their stomachs. This season (1921), whilst the Coniston Foxhounds were hunting on the fells, a couple and a half of hounds ran a fox in the direction of an earth on which some of the field were standing. About the same time, an otter suddenly ran out from some rocks near the main earth, and after going some distance, tucked in its head and forelegs, and actually rolled some yards downhill. We were on the opposite side of the valley at the time, but a very keen and experienced fox and otter hunter who was there, and witnessed the incident, said that he had never seen anything like it before in his life.
A name to conjure with in the annals of Lakeland « 138 » otter-hunting is that of the late Bobby Troughton. He was born on Fellside, Kendal, in 1836. In the early eighties he purchased three hounds, "Raleigh," "Ragman," and "Londesborough," and with these three hounds and a couple of terriers he began to hunt the local rivers. Having thus formed the nucleus of a pack, he gradually added to it and improved it, until the late Mr Courtenay Tracy, M.O.H., said there was not another pack like it in England. Bobby's heaviest otter was a big dog weighing 32 lb., and was killed in Rydal Lake. One of his most famous hunts took place in Lever's Water on the Coniston fells. Hounds met at 5 a.m. at the foot of Yewdale Beck, and striking a hot drag at once, went out towards the hills. Near the edge of the tarn they put their otter down, and he at once took to the water. For nine hours he kept hounds going, and it was not until some of the field volunteered to go to Coniston for a boat—no small undertaking—that Bobby was able to get afloat himself, and give his hounds a helping hand. At long last the otter attempted to land, and hounds collared him, thus earning their reward.


At one time in the north, packs of rough hounds were kept for hunting otter, marten, and foumart. One of the last of these packs to hunt in the Lake District belonged to the late Mr Fleming Green, of Grasmere. Anthony Chapman, who was his huntsman, and later hunted the Windermere Harriers for many seasons, is still hale and hearty, and delights in a "crack" about old times.
Another well-known Master in the north was the late Mr James Lomax, of Clayton Hall, Great Harwood, Lancashire.
His "Otter-hunting Diary" contains an account of the sport he enjoyed from 1829 to 1871, and is most interesting reading. Like Bobby Troughton in later years, he bred a very perfect pack of hounds of the rough-coated type. In 1871 rabies unfortunately broke out in his kennels, necessitating the destruction of all but three of the hounds. Being himself advanced in years, he made no attempt to start a new pack, despite the « 140 » many offers of hounds he received, and one cannot blame him. By the time he had got together another pack as good as the one he had lost, he would as he said himself have been too old to follow and enjoy the sport. Mr Lomax always met very early in the morning, often as soon as 3 a.m. He showed wonderful sport on Ribble, Lune, and many other rivers, and old men who can remember hunting with him, speak in glowing terms of the great hunts they enjoyed with his pack. In one respect Mr Lomax differed from present-day Masters, i.e., in the practice of "sacking" otters and removing them to more huntable waters. There are in the diary, several instances recorded of such otters having died, so that the practice was not a profitable one.
The most famous otter-hunter Scotland has ever seen was the late Mr Waldron Hill, of Murrayfield House, near Edinburgh.
When quite a young man he contracted consumption, and was told by his doctors that he had not long to live. Nothing daunted, however, « 141 » Mr Hill took to otter-hunting, and the sport agreed with him so well, that he hunted practically every river in Scotland, and lived to be far advanced in years.
When the West Lothian Foxhounds were in existence, Mr Hill used to run with them, and saw as much sport as most of the mounted brigade.
In "Field and Fern," The Druid wrote regarding Mr Hill: "Some years ago he had a pack of otterhounds in Monmouthshire, of the Welsh breed, smooth and white with yellow ears; for the last five years he has had black and tans, a cross between the bloodhound and rough Lancashire hound, which is used in that country for otter and foumart. Their nose is nearly equal to the Lancashire hound, who are unrivalled in this respect and never disposed to be tonguey. The bloodhound cross also makes them more savage in their worry, but they are often very unpleasant to manage in kennel. Mr Hill has found the foxhound fail in working up to his otter in a cold drag, but excellent on the line when the game is fairly « 142 » started. With him the southern hound has only failed from lack of constitution, which is injured by too much swimming."
Mr Hill used terriers of Welsh breed, which he got from the kennels of Mr Ramsay Williams, after the latter's death. These terriers weighed about 15 lb., and were bred as flat-sided as possible to enable them to squeeze into narrow places. They were fairly long on the leg, and were used for bolting fox, otter, marten, and foumart. Mr Hill's principal river was the Tyne, flowing through Haddingtonshire. Speaking of the South Esk, The Druid says: "Last August it was the scene of a very remarkable run, as the otter only touched the water twice for a few minutes throughout a run of eight or nine miles, and was eventually pulled down in the heart of one of the East Lothian fox-whins." Regarding a long drag with Mr Hill's hounds, The Druid says: "In '62 the hounds hit upon one at the Clutby Dam reservoir on the north side of the Pentlands, and hunted him through the sheep-drains right « 143 » over the Pentlands, down to the reservoir at St Catherine's. He had gone through it on the north side, and from there down the Glencorn burn, nearly to the North Esk. Leaving this for another burn across the country, he headed back to the reservoir at St Catherine's, where, on account of the water being too high, he could not be moved. This otter must have travelled nearly twenty miles during the night, and it was well for Mr Hill that his terriers were long-legged; and that he himself is always in condition summer or winter, or he would have seen nothing of the fun on that hot and very wet September morning." We wonder how far the members of a modern otter-hunting field would get, if asked to follow hounds on a hot drag for twenty miles? Not far we'll warrant, for most of them would swear that hounds were on a fox.
People who incautiously "tail" an otter are very apt to get bitten, and regarding this The Druid says: "In all these forays Mr Hill has never got heavily bitten himself; but many years ago, when « 144 » he was hunting on the Kenvy near Abergavenny, the otter came out of the water just before it was killed, made straight at the whip, who was a few yards off his master, shook him savagely by the trousers, and then passed on."
We have heard people say that an otter makes no splash when diving or otherwise entering the water. Certainly at times he does not make much of a disturbance, for his sinuous body is built for swimming, but when playing in the water, or when hunted, he splashes quite a lot. We were on one occasion watching the mouth of a drain on the river Lune, in which the terriers were baiting an otter. In front of this drain was a row of willow trees. Standing quietly a yard or so to one side of the drain entrance we at last saw the otter show himself. He stood at the drain mouth sniffing the air, the muscles working his thick "whiskers," giving his face a very puffed out appearance. Hearing or seeing some of the field on the opposite bank of the river he turned round and went back up the drain. A fairly long interval elapsed, and we « 145 » were just bending down to listen at the drain mouth, when, without the slightest warning the otter shot out, and leapt straight through the willow tree, to land in the water with a splash like a sack of oats. From where he took off, to the point where he hit the river, constituted a remarkable jump, and he must have been coming pretty fast when he shot out of the drain.
On another occasion at the same drain, which is a favourite resort of otters, the terriers were at work, and an opening had been made into the drain at some distance from the river. We were watching the drain mouth, and after a bit the otter showed himself, but went back. The bank where we stood was high, and there was a certain amount of rubbish in the way of dead branches, etc., partially covering the drain mouth. Being below the bank we could not see what was happening in the field, and we were greatly astonished when a big otter suddenly rushed over the edge of the bank, nearly on top of us, scrambled through the branches, and disappeared up the drain. The « 146 » terriers had bolted him in the field, and we, of course, were unaware of what was happening. This otter finally emerged at the drain mouth, but unlike his predecessor, took the water quietly below the willow trees.
In Walton's description of a morning's sport with Mr Sadler's "Otter-dogs," Sweetlips—one of the hounds—brings the carcass of the otter to "Venator." We have on several occasions seen a hound seize and carry a dead-beat otter ashore. This is easily done in the case of a 12 lb. or 14 lb. otter, but it is a different matter for a hound to handle a big, fighting dog otter. When a hunted otter is floating on top of the water, he often makes a considerable splash if he dives in a hurry.
Although perhaps not so good a climber as some other members of the weasel family, the otter is no slouch at negotiating steep, rocky ghylls, and can scramble about in a wonderful manner. It seems rather hard to account for the fact that in some seasons hounds kill a majority of dog otters, while in other seasons the total is chiefly made up of « 147 » bitches. Where you find a bitch otter, there is often a dog within a mile or so, either up or down stream; and no doubt the two of them keep that particular stretch of water free from other lutrine intruders.
Scent and its vagaries will no doubt always be a mysterious problem. How often have we seen hounds able to hunt quite well amongst the undergrowth, yet when they reached an open expanse of sand where the seal of an otter was plainly visible, they have crossed it without a single hound speaking. An instance of this comes to mind during the season of 1921, when hounds ran well across country, whereas on a sand-bank, literally padded flat with otter tracks, never a hound opened.
Although hounds may sometimes travel a long way up-stream without touching a drag, that does not always signify that you will not find. An instance of this comes to mind when we were hunting a small hill-stream. Hounds had covered some miles of water without a sign of a drag, and the field was becoming rather discouraged, when « 148 » suddenly the pack opened in no uncertain manner, and began tearing at a holt on the bank. While hounds were thus occupied, the otter bolted and went downstream, and after a short hunt was accounted for. Until reaching the spot where hounds marked, there was little or no lying ground, and seeing that there was also no up-stream drag it pointed to the fact that our otter had travelled over a neighbouring watershed, and had entered the holt on his journey downstream. It is always well to remember that an otter may be found anywhere, and because there happens to be no drag up-stream that does not mean to say that you may not find when you reach the head waters.
Regarding the agility and jumping powers of otters we remember hounds finding an otter lying rough, which, after a certain amount of dusting up and down stream, jumped a wall into a road, passed under a motor car standing there, and went over another wall into the field beyond. Leaving the field it scaled a third wall before returning to the water. Eventually it took to some extensive « 149 » coverts, and after running a ring through them, it was bowled over by hounds in the open as it was making its way back to the river. That an otter knows every inch of ground over which he has once travelled is made quite apparent to those who do much otter-hunting.
We have, in a previous chapter, told of an otter which travelled ten miles overland from one stream to another, going straight to the various smoots through the walls which barred its passage. In an emergency, too, an otter makes up his mind pretty quickly. On one occasion the terriers got to their otter in a drain, and after opening the latter, the otter backed out. The drain lay parallel to a hedge, and like a flash the otter darted through this, ran down behind it, and was into another underground retreat before anyone had time to realise his game.
As a rule, if two otters are put down together, the one which is not being hunted will promptly make itself scarce. We remember on one occasion, however, when hounds were hunting a bitch otter, « 150 » the dog hung about in plain sight under a bridge, and remained there until the bitch was accounted for, after which he himself suffered the same fate.
Otter-hunting is the least artificial of our British field sports. The otter is a wild animal, living the same free life that he has done for generations, and we have yet to learn a good deal concerning him. Being a great wanderer, he is here to-day and gone to-morrow, and his hunting provides more "glorious uncertainty" than the chase of any other beast. Before you can hunt him you must find him, but whereas with deer, fox, and hare, the finding is often the easiest part of the business, in the case of the otter it is the most difficult. In a previous chapter we have made brief mention of otter-hunting dress. In these days blue is the popular colour for Hunt livery, the material most favoured being woollen serge. We wonder how modern otter-hunters would like to wear the dress mentioned by Blaine, i.e., a green dress turned up with red, fur cap with gold band, and waterproof hip-boots decorated with red or gold tassels.
It was Somervile in The Chase who coined the phrase "sly goose-footed prowler," and gave to the world one of the best accounts of an otter-hunt ever penned. Otter-hunting seems to have been little catered for in the matter of songs pertaining to the sport. No doubt there are many purely local ditties concerning the doings of various packs, but few songs of real worth have made their appearance. In "The Poetry of Sport" by Hedley Peek, we find one or two, and in the "Otter-hunting Diary" of Mr James Lomax there are a couple of Lancashire otter-hunting songs. One of these songs is in dialect, and we take the liberty of quoting a verse or two for to anyone who understands broad Lancashire they convey a lively description of the sport. The song is entitled "The Hunt in the Hodder." In the first verse the narrator goes to the meet:
After a good drag, hounds mark their otter in his holt, and Crab the terrier is sent in.
Hounds swim their otter for some time until at last he takes refuge in a holt.
Hounds eventually account for their otter, and the song finishes with:
A rather amusing incident occurred some years ago when we were whipping-in to the now disbanded Lake District Otterhounds. Whilst waiting at Lakeside for the boat that runs up Lake Windermere, a char-a-banc load of trippers arrived, to whom the sight of a pack of otterhounds was evidently a novelty. Before we knew what was happening, the crowd of sightseers had formed a ring round hounds, each member of the party producing a song book. There then rose on the air the well-known refrain "John Peel." The old huntsman listened whilst they sang the first verse, then suddenly exclaimed "Give it more weft! give it more weft!" Isaac evidently thought that their efforts compared badly with the way in which the old song is sung by fox-hunters in Cumberland or Westmorland.
In addition to being the least artificial of our British field sports, otter-hunting affords unrivalled opportunities for those who love to watch the work of hounds. It is more popular now than it ever was, yet there is still ample room for many more « 154 » packs before our rivers and lakes are thoroughly hunted as they should be. The more otters you kill the more you will have, for riparian owners and tenants are for the most part quite willing to afford protection to Lutra, when they know that a keen huntsman and a killing pack of hounds are hunting their waters regularly throughout the season.
In conclusion we will finish with the old south-country toast "Death to dog otters! Long life to the little bitches!"

FINIS
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H
I | I | J | K | L | M | N | O
P | R | S | T | U | W | Y | Z
PRINTED IN GREAT BRITAIN AT
THE NORTHUMBERLAND PRESS LIMITED, NEWCASTLE-UPON-TYNE
Transcriber Note
Illustrations moved so as to not split paragraphs. On page 114, braches was changed to raches.
End of Project Gutenberg's The Book of the Otter, by Richard Clapham
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK THE BOOK OF THE OTTER ***
***** This file should be named 52071-h.htm or 52071-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/5/2/0/7/52071/
Produced by Tom Cosmas and The Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was
produced from images generously made available by The
Internet Archive)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will
be renamed.
Creating the works from print editions not protected by U.S. copyright
law means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works,
so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United
States without permission and without paying copyright
royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part
of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm
concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark,
and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive
specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this
eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook
for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports,
performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given
away--you may do practically ANYTHING in the United States with eBooks
not protected by U.S. copyright law. Redistribution is subject to the
trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
START: FULL LICENSE
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full
Project Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at
www.gutenberg.org/license.
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or
destroy all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your
possession. If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a
Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound
by the terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the
person or entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph
1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this
agreement and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the
Foundation" or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection
of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual
works in the collection are in the public domain in the United
States. If an individual work is unprotected by copyright law in the
United States and you are located in the United States, we do not
claim a right to prevent you from copying, distributing, performing,
displaying or creating derivative works based on the work as long as
all references to Project Gutenberg are removed. Of course, we hope
that you will support the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting
free access to electronic works by freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm
works in compliance with the terms of this agreement for keeping the
Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with the work. You can easily
comply with the terms of this agreement by keeping this work in the
same format with its attached full Project Gutenberg-tm License when
you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are
in a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States,
check the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this
agreement before downloading, copying, displaying, performing,
distributing or creating derivative works based on this work or any
other Project Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no
representations concerning the copyright status of any work in any
country outside the United States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other
immediate access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear
prominently whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work
on which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed,
performed, viewed, copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and
most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no
restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it
under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this
eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the
United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you
are located before using this ebook.
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is
derived from texts not protected by U.S. copyright law (does not
contain a notice indicating that it is posted with permission of the
copyright holder), the work can be copied and distributed to anyone in
the United States without paying any fees or charges. If you are
redistributing or providing access to a work with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the work, you must comply
either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 or
obtain permission for the use of the work and the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any
additional terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms
will be linked to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works
posted with the permission of the copyright holder found at the
beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including
any word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access
to or distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format
other than "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official
version posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site
(www.gutenberg.org), you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense
to the user, provide a copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means
of obtaining a copy upon request, of the work in its original "Plain
Vanilla ASCII" or other form. Any alternate format must include the
full Project Gutenberg-tm License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
provided that
* You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is owed
to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he has
agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments must be paid
within 60 days following each date on which you prepare (or are
legally required to prepare) your periodic tax returns. Royalty
payments should be clearly marked as such and sent to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the address specified in
Section 4, "Information about donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation."
* You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or destroy all
copies of the works possessed in a physical medium and discontinue
all use of and all access to other copies of Project Gutenberg-tm
works.
* You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of
any money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days of
receipt of the work.
* You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work or group of works on different terms than
are set forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing
from both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and The
Project Gutenberg Trademark LLC, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark. Contact the Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
works not protected by U.S. copyright law in creating the Project
Gutenberg-tm collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may
contain "Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate
or corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other
intellectual property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or
other medium, a computer virus, or computer codes that damage or
cannot be read by your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium
with your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you
with the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in
lieu of a refund. If you received the work electronically, the person
or entity providing it to you may choose to give you a second
opportunity to receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If
the second copy is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing
without further opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO
OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of
damages. If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement
violates the law of the state applicable to this agreement, the
agreement shall be interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or
limitation permitted by the applicable state law. The invalidity or
unenforceability of any provision of this agreement shall not void the
remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in
accordance with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the
production, promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, harmless from all liability, costs and expenses,
including legal fees, that arise directly or indirectly from any of
the following which you do or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this
or any Project Gutenberg-tm work, (b) alteration, modification, or
additions or deletions to any Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any
Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of
computers including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It
exists because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations
from people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future
generations. To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation and how your efforts and donations can help, see
Sections 3 and 4 and the Foundation information page at
www.gutenberg.org
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent permitted by
U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is in Fairbanks, Alaska, with the
mailing address: PO Box 750175, Fairbanks, AK 99775, but its
volunteers and employees are scattered throughout numerous
locations. Its business office is located at 809 North 1500 West, Salt
Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email contact links and up to
date contact information can be found at the Foundation's web site and
official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND
DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular
state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To
donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project
Gutenberg-tm concept of a library of electronic works that could be
freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and
distributed Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of
volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as not protected by copyright in
the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not
necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper
edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search
facility: www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.